Chmod Command In Linux For Directory

Ownership And Permissions

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World
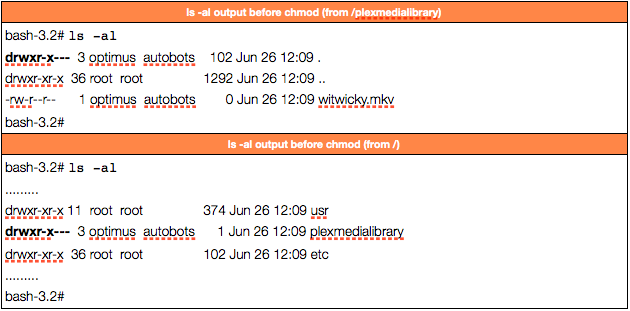
Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

Changing File Permissions In Linux The Chmod Command By Saswat Subhajyoti Mallick Medium
/GettyImages-1021092796-ea8c63ee76f84bd5bf98c4222337fbb4.jpg)
How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux
Chmod permission file_name There are two ways to define permission:.

Chmod command in linux for directory. D rwxr-xr-x Popular CHMOD Commands (TOP ) chmod 777. You can set the umask values in /etc/profile or in ~/.bashrc. To selectively change permission , use find command to get the directories or files and then change mode.
In this tutorial, we will discuss the basics of this command as well as provide examples explaining how it can be used in various scenarios. For instance, if you run. If the directory is part of the system or an installed package managed by rpm you can find out which package it is part of with rpm -qf /directory and then can try rpm -qV <package> (verify) to see what the installed permissions settings were.
One set for the owner of the file, another set for the members of the file’s group, and a final set for everyone else. The chmod command in Linux is used to change file and directory permissions using either text (symbolic) or numeric (octal) notation. Now if we use chmod, it does not allow to modify root permission # chmod -c --recursive 755 / chmod:.
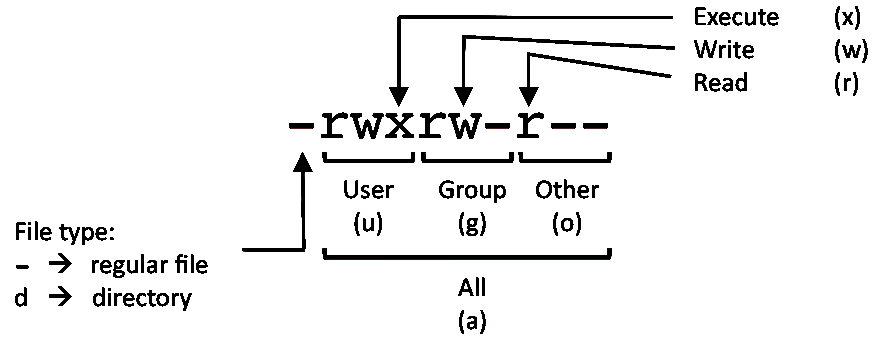
Chmod Command in Linux Linux File Permission Introduction to Linux File Permission. By using this command, we can set the read, write, and execute permissions for all three of the permission groups (Owner, Group and Other) in Linux. The permissions control the actions that can be performed on the file or directory.
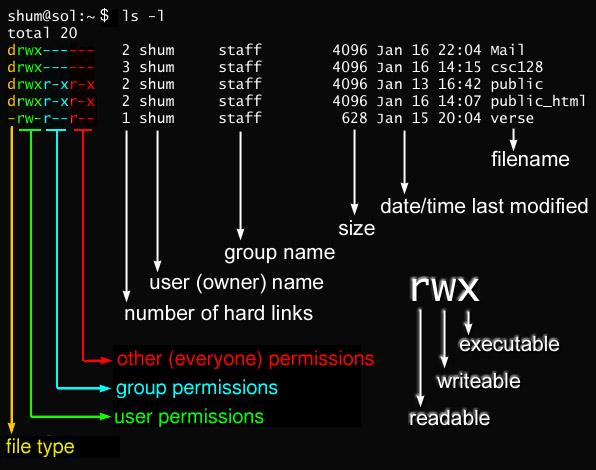
Every file in the Linux / macOS Operating Systems (and UNIX systems in general) has 3 permissions:. H ow do I use chmod and chown command under Linux / Unix operating systems?. Rwxrwxrwx ) to see its value in other formats.
It is dangerous to operate recursively on '/' chmod:. If you are using the octal numbers in chmod , give 1 before you specify other numbered privileges, as shown below. Chmod stands for change mode, which changes the file or directory mode bits.
Setting File Permissions in Command Line. You can also create a directory and set permissions at the same time. Myfolder the user owning myfolder will be username.
The general syntax to recursively change the file’s permissions is as follows:. As you might remember, the default file permission value is 0644, and the default directory’s is 0755. Linux File Permission :.
We run the chmod command command to change file access permissions such as read, write, and access. Actually, chmod Command in Linux plays a greater role to keep all the files and directories of the system safe and secure so that no unauthorized person. Linux divides the file permissions into read, write and execute denoted by r,w, and x;.
$ chmod u+X *. If you are new to Linux, and are looking for a way to change file/directory permissions through the command line, you'll be glad to know there exists a command - dubbed chmod - that lets you easily do this. It is also used to change special mode flags.
Chmod ugo+rwx foldername to give read, write, and execute to everyone. You can use -R with chmod for recursive traversal of all files and subfolders. After that, you will be able to run it without using the sh or bash commands.
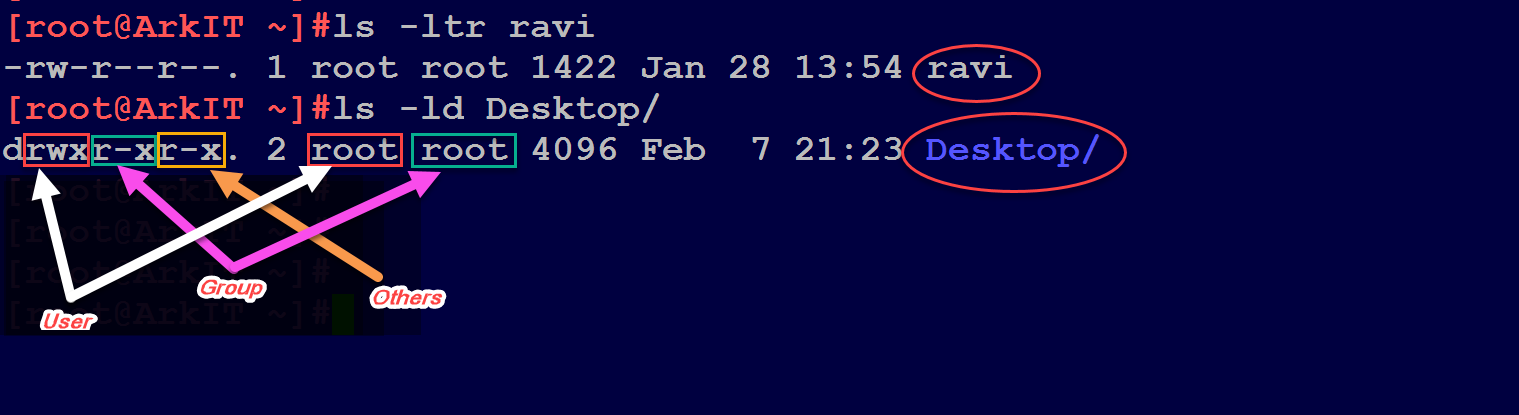
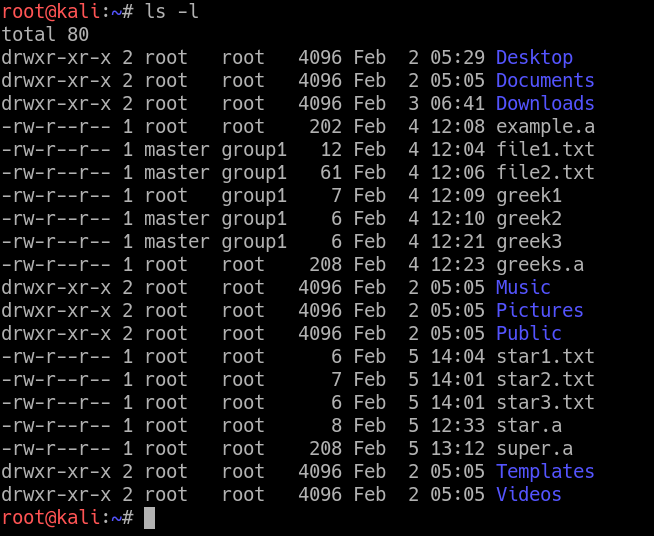
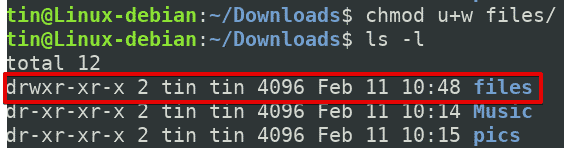
The weird strings you see on each file line, like drwxr-xr-x, define the permissions of the file or folder. To put it simply, use chmod command to change the file or directory permissions. After changing a directory's mode to 755 the folder's mode will be displayed in Unix style file lsting as:.
In the terminal, the command to use to change file permission is chmod. The chmod command allows you to change the permissions of files using symbolic or numeric mode. Chmod command is useful to change permission for Files and folders in Linux/Unix.
In Unix and Unix-like operating systems, chmod is the command and system call which is used to change the access permissions of file system objects (files and directories). Replace directory with the directory path that holds the files and subdirectories you want to configure. As all Linux users, you will at some point need to modify the permission settings of a file/directory.
The chmod command is used in Linux to change these permissions. These permissions are given to file/folder to provide a secure environment to the OS, efficient management of a file and high-level access to the users accessing the files/ folders. The chmod command A normal consequence of applying strict file permissions, and sometimes a nuisance, is that access rights will need to be changed for all kinds of reasons.
777 ) or symbolic notation (e.g. It is used to change the permission for files and folders. More Information on.
Chmod is a very helpful command to change the file permissions of a file or a folder in any UNIX-like operating system. The first step is to create a new text file with .sh extension using the following command. The chmod command allows you to change the permissions on a file using either a symbolic or numeric mode or a reference file.
We simply pass the directory name to chown instead of a filename. We use the chmod command to do this, and eventually to chmod has become an almost acceptable English verb, meaning the changing of the access mode of a file. It takes the following syntax:.
There are three sets of permissions. To change directory permissions for everyone, use “u” for users, “g” for group, “o” for others, and “ugo” or “a” (for all). The name is an abbreviation of change mode.
Sudo chmod u+w myfolder to add the write permission to the username user. Chmod is a great Linux command for manipulating file and directory permissions. Chmod -R 755 directory chmod 777:.
In Linux, you can easily change the file permissions by right-clicking the file or folder and select “Properties”. This type of restriction is useful for effective file/folder management, securing system and providing a level …. The command is relatively simple to use and involves using.
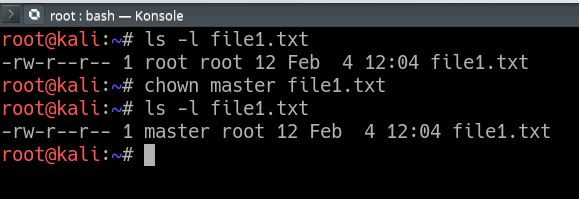
Chmod -R 755 can change the permissions recursively but it will change same permissions for everything , folders,subfolders and files. If you want to change the user owning this file or directory (folder), you will have to use the command chown. This command will change the user ownership of all files beginning with the letter “c.” sudo chown mary c*.* All of the files will now have mary as their owner.
The default umask value is subtracted from the overall file/directory default value. Linux file permission is a very important aspects in terms of security issues for the system administrator of Linux Operating System. This command will give read, write and execute permission to the owner, group and public.
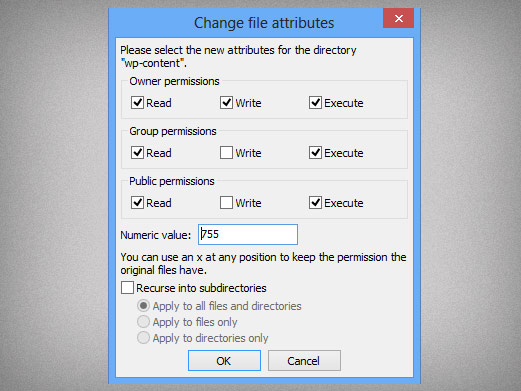
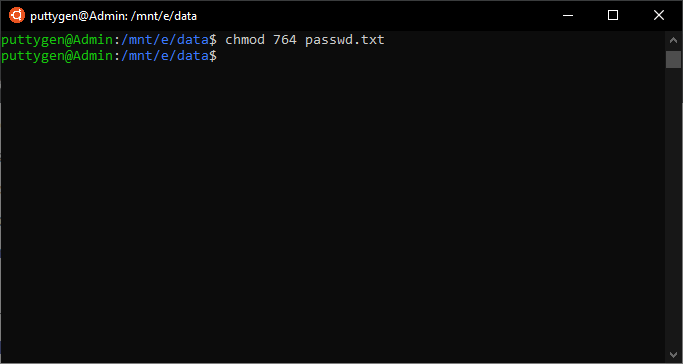
To change permission using the Linux chmod command we have to follow some syntax and rules. If you want to change the mode to 777, you can use the command like this:. Chmod Calculator is a free utility to calculate the numeric (octal) or symbolic value for a set of file or folder permissions in Linux servers.
The owner, group members and others. Note that none of the group ownerships have been changed. + for adding and – for removing.
You can change file permissions in this format:. Following is a sample of ls -l command output. Once you create a new directory in Linux, then you can change permissions and create folders within the directory.
Chmod stands for “Change Mode” and is used to modify the permissions of files and directories in a Linux based system. Let us understand CHMOD and CHOWN commands in detail. The chmod command stands for change mode… and it’s used to limit access to resources….
At the Unix prompt, Fred should type. Chmod (change mode) is one of the most frequently used commands in unix or linux operating system. Chmod is command which changes permission of a file or folder for particular user or group as per instructions provided.
Go into a folder, and run the ls -al command. Linux Tutorial for Beginners && Git Tutorial for Beginners. The basic syntax is:.
Chmod means ‘change mode’ and it changes file or directory mode bits (the way a file can be accessed). In this tutorial, I am going through the steps to create a bash script and to make the script executable using the chmod command. Use --no-preserve-root to override this failsafe Linux Permissions Syntax.
Let’s say you are currently in the root directory of your Unix-like system and you want to change the file permissions of a folder and all of the other files and sub-directories present inside that folder. The request is filtered by the umask. In Linux, who can do what to a file or directory is controlled through sets of permissions.
In Linux, you will often need to make use of the chmod command. # alias chmod='chmod --preserve-root' and also add this to your /etc/bashrc or individual user's .bashrc file for permanent changes. The 'chown' command can change the ownership of a file/directory.
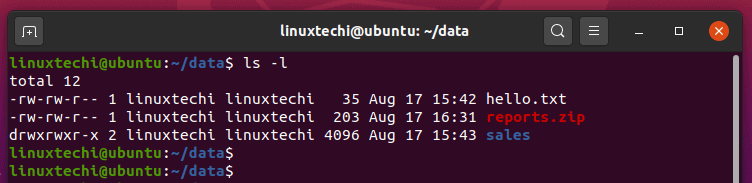
The command can accept one or more files and/or directories separated by space as arguments. To know about the access permissions of a file or directory, use the ls -l command as shown below:. Chmod Modifies File Permissions.
$ chmod -R 755 directory-name/ 7. Chmod a=r foldername to give only read permission for everyone. In short, “chmod 777” means making.
To recursively operate on all files and directories under a given directory, use the chmod command with the -R, (--recursive) option. Use the following commands:. This page explains how to use chmod and chown command on Linux or Unix-like systems.
Using Options with chmod and chown Commands. The chmod command is used to change the file or directory access permissions. This command changes the mode of Fred's home directory (represented by the ~), giving permission to all users to get to files in that directory.
Linux - Solution 4:. On a very basic level, file and directory permissions play a vital role in the security of a system. You can use chmod in the command line to change file or directory permissions on unix or unix-like systems such as linux or BSD.
By - Linux tutorial - team The X (that is capital X, not small x!) is ignored for files (unless they are executable for someone already) but is used for directories. $ chmod OPTIONS MODE filename Only the root user or a regular user with sudo privileges can change file or directory permissions. The name is an abbreviation of change mode.
Then you can execute. 15-05-19 In Unix-like operating systems, the chmod command is used to change the access mode of a file. Ls -l mary c*.* Let’s change the ownership of a directory.
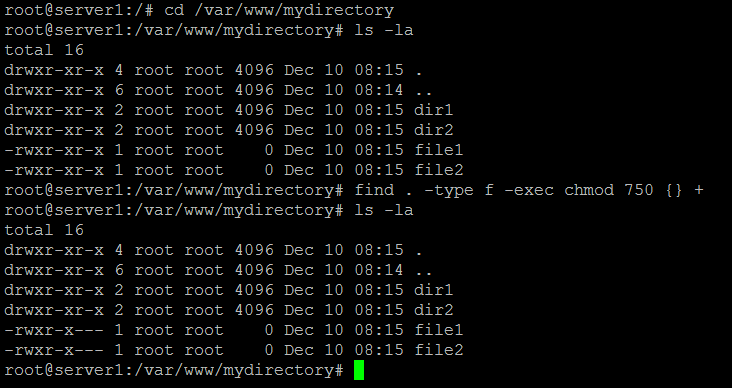
Is there a way to undo a chmod command on a directory in CentOS ?. This document describes the GNU / Linux version of chmod. Sudo find directory -type d/f -exec chmod privilege {} \;.
Below is a list of numerical permissions that can be set for the user, group, and everyone else on the. You can then revert to those with chmod manually or with rpm --setperms as stderr. How to use Check the desired boxes or directly enter a valid numeric value (e.g.
In Linux/Unix like operating system, the chmod command is used to change the access mode of a file. Creating a Bash File. Chmod command is used to change access permission of files and directories in Linux operating systems.chmod stands for change mode.Access permissions specify whether a user account or group can read, write, or execute a given file and directory.
Therefore, Joe can access any file, of which he knows the name, in Fred's home directory. When you create a file or directory on Linux systems, it comes with default permissions. The command that executes such tasks is the chmod command.
After user level we have provide what needs to be done i.e. This Linux option allows you to change permissions or owners of all files and subdirectories inside a specific directory. Chmod command in Linux with examples Last Updated:.
The permissions on a file can be changed by 'chmod' command which can be further divided into Absolute and Symbolic mode;. Option is an additional command to change the output of a command. In this, the 9 characters from 2nd to 10th position represents the permissions for the 3 types of users.
In Unix-like operating systems, the chmod command sets the permissions of files or directories. Chmod -R MODE DIRECTORY. File/Directory permission is either Read or Write or executable for either user or group or others.
Chmod command is followed by which level user i.e. The basic syntax includes using the find command to locate files/directories and then passing it on to chmod to set the permission:. We will explain the modes in more detail later in this article.
One of the most popular options that you can combine with chmod and chown is -R (Recursive). You might have heard of chmod 777. Chmod has two operating modes:.
How to Use the chmod Command in Linux Command Syntax. The Linux command to change permissions on a file or directory is chmod, which we like to read as change file mode. It’s a same as using your mouse to right-click a file or folder and selecting the permission tabs and.
The command CHMOD stands for change mode, and this is used to change the permission of a File or Directory.The Command CHOWN stands for Change Owner and this is used to change the ownership of a File or Directory. $ ls -l sample.sh -rwx-rw-r-- 1 matt deploy 94 Oct 4 03:12 sample.sh. To create directories in Linux, you can open Terminal and use the command line with the mkdir command.
How to use chmod?. Use chmod command to set the sticky bit. Using symbols (alphanumerical characters) using the octal notation method.
The first 7 sets the permissions for the user, the second 7 sets the permissions for the group, and. There will be a Permission tab where you can change the file permissions. The chmod command in Linux/Unix is abbreviated as CHange MODe.
Use the chown command to change file owner and group information. The chmod command is used to define or change permissioins or modes on files and limit access to only those who are allowed access… It changes the mode of each FILE to MODE…. Change execute permission only on the directories (files are not affected) On a particular directory if you have multiple sub-directories and files, the following command will assign execute permission only to all the sub-directories in the current directory (not the files in the current directory).
The example below, gives rwx permission to user, group and others (and also adds the sticky bit to the directory).

Chmod Calculator Chmod Generator Chmod Command

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs J72hjomdluhqe6xjivy M6yrjmkqx9x3z3ps Rpnb8by3w7z Usqp Cau

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/mkdir-linux-5c4763ffc9e77c00014ae996.png)
How To Create Directories In Linux With The Mkdir Command

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission
How To Create A Read Only File In Your Home Directory In Unix Quora

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Youtube

Chmod Cheatsheet Linux

Understanding Basic File Permissions And Ownership In Linux The Geek Diary
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube

Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech

Linux Users And Groups Linode

How To Set File And Directory Permission In Linux Using Chmod Linux Syntax Settings

Delete Remove A Directory Linux Command Nixcraft

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)
Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu

Change File And Folder Permission On Ubuntu Chmod Chown Command In Linux Youtube
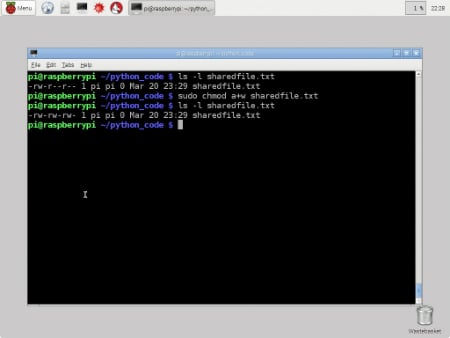
Working With File Permissions On Your Raspberry Pi Dummies

Lock Usb Devices With Chmod Command In Linux Tutorials

Linux Commands Chmod Cloudaffaire

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

Linux Unix Permissions And Attributes Linuxsecrets
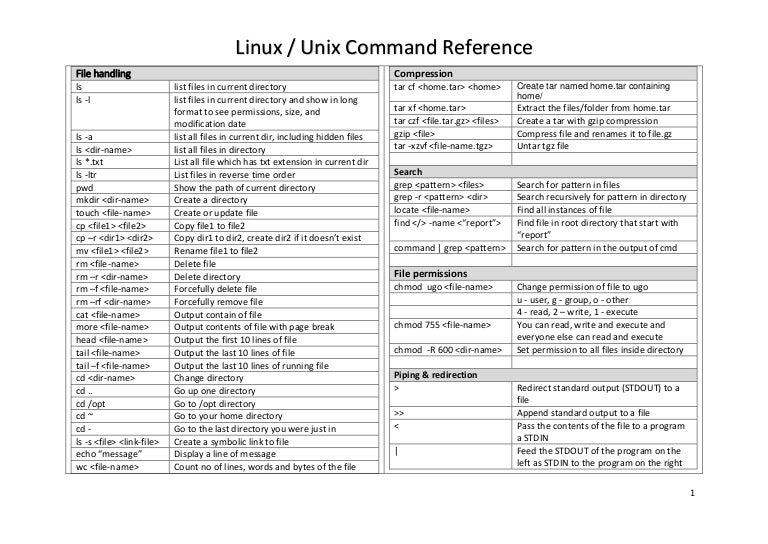
Unix Linux Command Reference

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux Basic Linux Permission Linux File Permission Wiz Maverick Benisnous
Chown Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission
Javarevisited 10 Example Of Chmod Command In Unix Linux
/create-directories-linux-mkdir-command-3991847-55ea75a52f7842a2af0fdfe0b7470270.gif)
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsrj1qp4zwyexf6er5nh8l9pmjynafoe C3vq Usqp Cau

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode

Linux Command Line Cheatsheet

Linux Chmod Command Utility Software Computer File

7 Linux Change Permissions Of Files Directories Using Chmod Commands Youtube

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Write Access Chmod Permissions

File Rights Management In Linux Programmer Sought

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders
Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected

How To Change Permissions And Owners Via Linux Command Line
Chmod Chown Wsl Improvements Windows Command Line
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq1nsq3kxri7ryrifobs2rfobawbv4hezfw9 Ldf4feblahyn09 Usqp Cau
Lab 4 Manuel Montiel S Eportfolio

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Linux File Permission Change By Chmod Command In Linux Guide For Beginners

Linux Commands 5 File Permission Chmod Youtube

8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut

Command Line I Can T Change Mode For Some Directories Using Chmod Ask Ubuntu

Linux Command Line Basics Part 4 I Have A Pc I Have A Pc

Directory How Can I Change Permissions Of A Folder Including Its Enclosed Files And Subdirectories Ask Ubuntu
Linux Commands Cheat Sheet Linux Training Academy

08 Unix Linux Shell File Directories Permission Chmod Command Youtube

Unix Permissions
Chmod Command Understanding How To Grant File Permissions
How To Chmod Files Only On Linux

How To Copy Files Using The Install Command On Linux
What Is Chmod How To Use Chmod For Wordpress File Permissions
Chown Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Chmod Command In Unix Unix File Permissions Chmod With Examples Chwn Command Chgrp Command Unmask
Top 50 Linux Commands With Example
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Linuxize
Solved This Is In Linux While Logged In As A Regular Use Chegg Com
Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs Trmaopb41lzfo2wl Mi6olorurkywaddbudhnw Ne1mor3ct Usqp Cau

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices
9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux

Permissions Why Use Chmod Instead Of Chmod U Rw Go R Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Understanding Linux File Permissions With Chmod Umask Chown And Chgrp Liquidon Net
Q Tbn 3aand9gcr2lfpzbutqythmvbwafnxvyggqfj7hnw6fhh Kcozkk8m5 V7o Usqp Cau

Linux Tutorial

Solved Outcome Unix And Your First Program 1 The Comman Chegg Com

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions

Use Of Chmod Command In Linux Devopsdex

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

How To Run A Script In Linux Nixcraft

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

Linux Command Line Basics Part 4 I Have A Pc I Have A Pc

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Solved Problem 7 12 Points Answer The Following Questi Chegg Com

How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct
Change File Permissions Recursively Linux Linux Hint

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Chmod Wikipedia

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks



