Chmod Give All Permissions To All Users
2

Solved Chmod Can Be Used To Change The Mode Of The File Chegg Com

How To Give Read Write Permissions To A Folder In Ubuntu Code Example
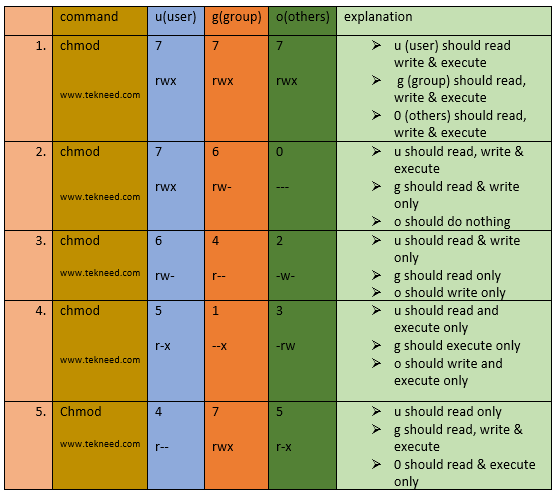
How To Set And Manage File Permission In Linux Part 1
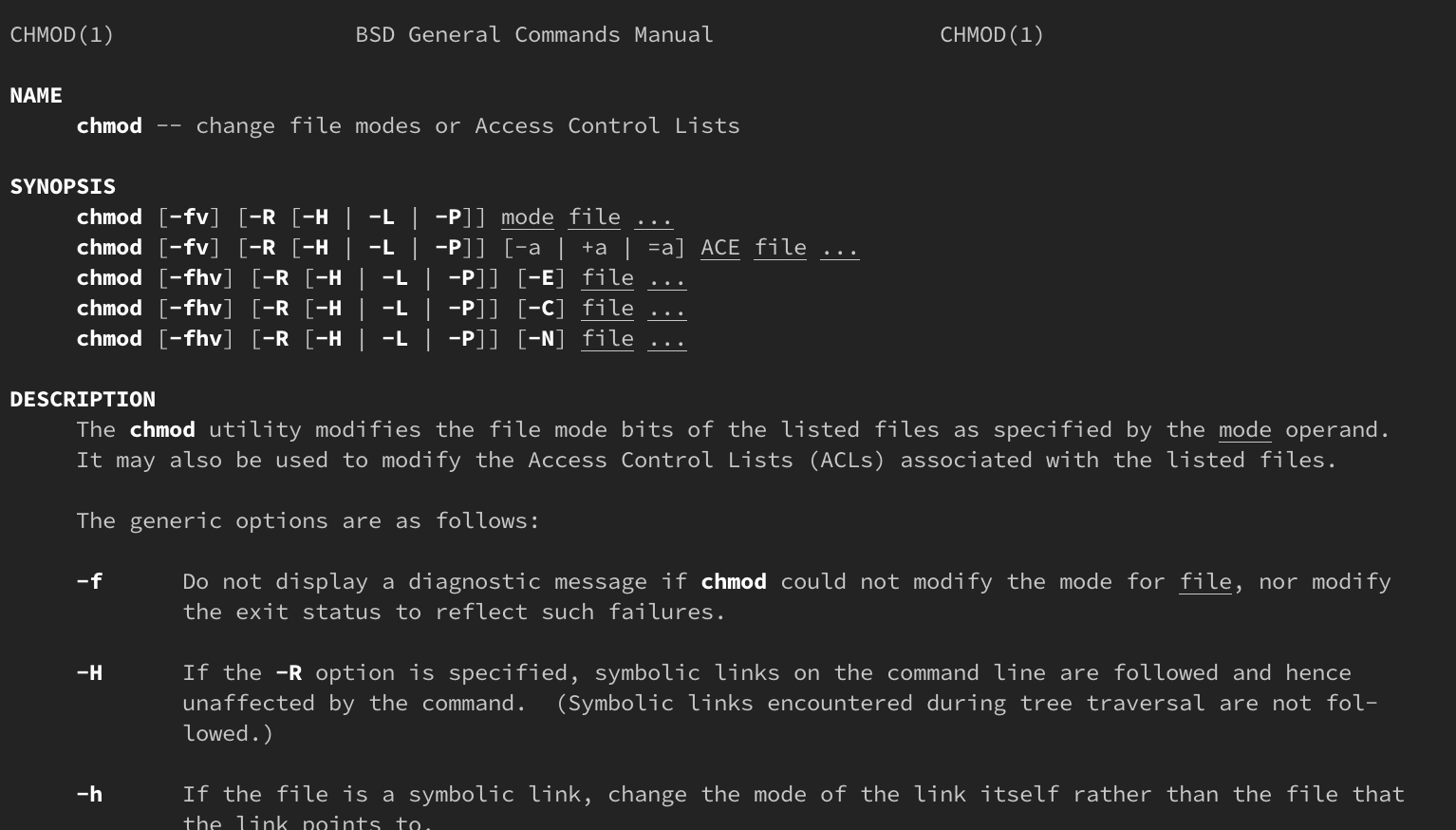
How Do Linux Permissions Work
%20access%20permission%20%EC%98%88)%20chmod%20644%20test.jpg)
Permissions Why Use Chmod Instead Of Chmod U Rw Go R Unix Linux Stack Exchange
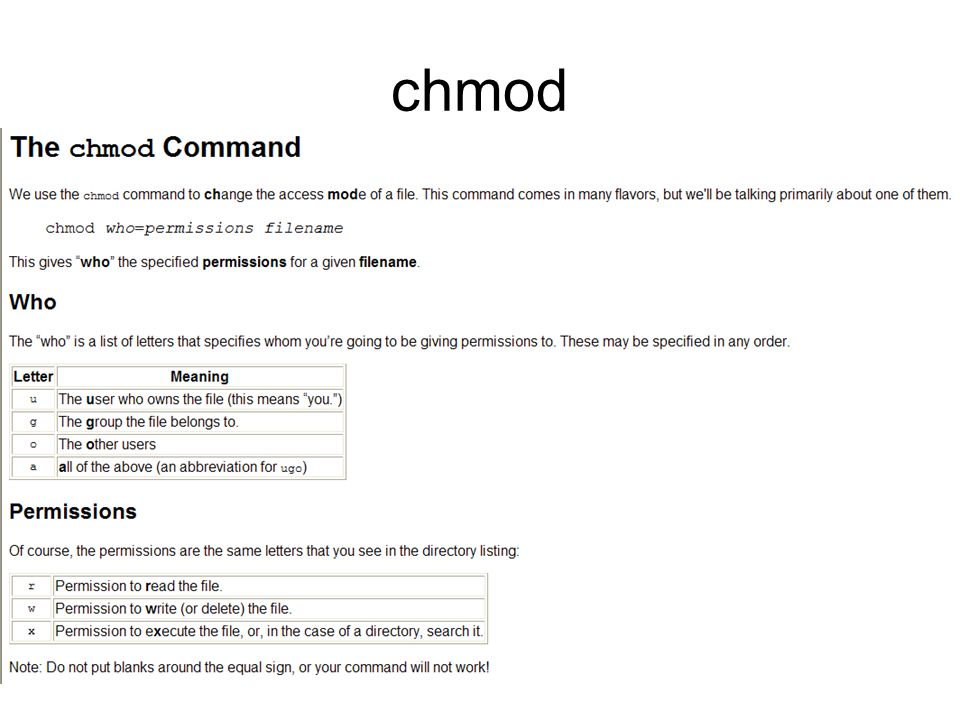
The operator determines whether to add (+), remove (-) or explicitly set (=) the particular permissions.

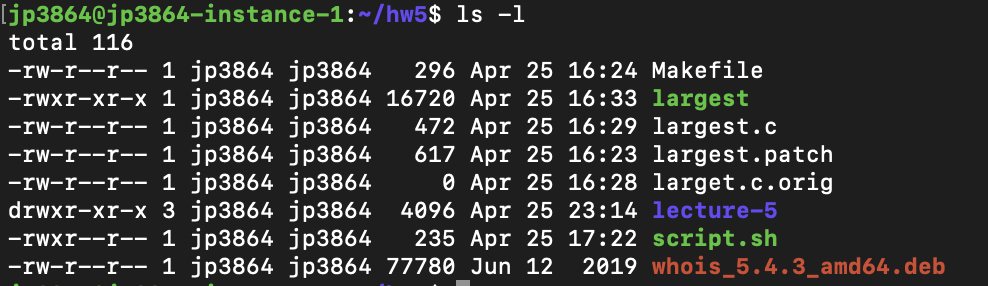
Chmod give all permissions to all users. Edited Jun 10 ’11 at 19:57. The chmod command allows you to change the permissions of files using symbolic or numeric mode. There even is a shorthand notation – a – to set permissions for all references.
Mykyta Dolmatov / Getty Images. Chmod is command which changes permission of a file or folder for particular user or group as per instructions provided. Give the file’s owner read, write and execute permissions, read and execute permissions to group members.
If chmod a+w filename, chmod +w filename and chmod ugo+w filename are alternative to each other then why not just use +w – Ravi Sevta Mar 10 '18 at 13:04. In this instance, the file owner is gaining read and write access, while the user group and other users are gaining read access. There you’ll see al.
Using symbols (alphanumerical characters) using the octal notation method. The modes include permissions and special modes. Sudo chmod -R 755 /www/store Each number have meaning in permission.
The leftmost digit represents the permissions for the owner. (Recursively) will cause all files and directories within (underneath) the file/directory whose permissions are being changed to take those permissions. If you do not specify a permission following =, the chmod command removes all permissions from the selected field.
What does chmod 755 do?. Sudo chmod g+w myfolder. Here are some examples of how to use the chmod command in numeric mode:.
The third set of flags specifies the permissions that are to be removed, applied, or set:. First create some empty files:. To remove permissions to do anything.
Meanwhile, since group and others are only allowed to read the file, we give them 4. Recursively (-R) Change the permissions of the directory myfiles, and all folders and files it contains, to mode 755:. The exact command is.
Here are a few examples of chmod usage with letters (try these out on your system). I actually give group write permissions as well, for users which need to modify content, such as users used to deploy code. For example, to grant execution permissions for other users to a directory (mydir) and all the subdirectories it contains, you would enter:.
The default umask is applied when creating a new file inside of a WSL distribution from Windows. To give owner, group and everyone else permission to execute file:. The chmod command allows a user to change the permissions of a file/directory.
The rightmost digit represents the permissions for the others. Chmod +x filename.shto make filename.sh executable. But if you want to add this user to the group associated with "myfolder", you can run.
If you want to change the permissions for all three kinds of users at the same time, you can use it in the following. Group permissions − The group's permissions determine what actions a user, who is a member of the group that a file belongs to, can perform on the file. Creating a new file.
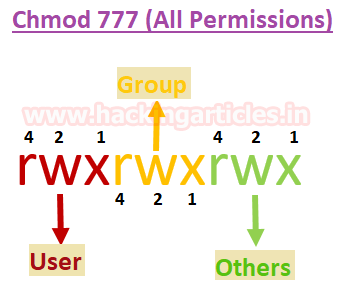
Command chmod 666 means that all users will have read and write permissions. So if you want to give all permissions (rwx) to a user, we need to add read (4), write (2), and execute (1). Group can read only;.
Other (world) permissions − The permissions for others indicate what action all other users can perform on the file. The chmod command (change mode) is a shell command in Linux. This permission give you the authority to open and read a file.
Chmod +x adds the execute permission for all users to the existing permissions. We will use 777 $ chmod 777 file. As all Linux users, you will at some point need to modify the permission settings of a file/directory.
$ chmod 700 executable Give All Permissions To All Roles. If you truly want any user to have full permissions on all files under directory/ (which may be OK if this is your personal computer, but is definitely not recommended for multi-user environments), you can issue this:. This is where Permissions set in, and they define user behavior.
$ chmod -R g+rx /var/www. Chmod permission file_name There are two ways to define permission:. Chmod a=r document.docx 5.2.
It means giving all (user+group+world) write permission to the all the files in recursive manner:. To use chmod, the user must be the owner of the file. The syntax is as follows:.
The u flag sets the permissions for the file owner, g refers to the user group, while o refers to all other users. $ chmod -R 600 /opt/lamp Read By Others But Can Not Edit. We may want to read by the owner group but not changed.
Symbol Meaning u user g group o other a all r read w write (and delete) x execute (and access directory) + add permission-take away permission # remove read write and execute permissions # on the file biglist for the group and others chmod go-rwx exam.pdf # give read and write permissions on the file. Therefore any Windows app accessing Linux files will have the same permissions as the default user. How to Change Groups of Files and Directories in Linux.
Every file and directory in your UNIX/Linux system has following 3 permissions defined for all the 3 owners discussed above. Chmod -R a+rX * click below button to copy the code. To make the document read-only for group and others, we can use:.
Examples chmod 644 file.htm. At the Unix prompt, Fred should type. The a flag has the same effect as specifying the ugo flags together.
Using letters is easier to understand for most people. Probably one of the most used case of chmod is to give a file the execution bit. It means giving group write permission to the all the files.
User@host:/home/user$ touch file1 file2 file3 file4 user@host:/home/user$ ls -l total 0 -rw-r--r-- 1 user user 0 Nov 19 :13 file1 -rw-r--r-- 1 user user 0 Nov 19 :13 file2 -rw-r--r-- 1 user user 0 Nov 19 :13 file3 -rw-r--r-- 1 user user 0 Nov 19 :13 file4. Therefore, Joe can access any file, of which he knows the name, in Fred's home directory. After user level we have provide what needs to be done i.e.
The basic syntax is:. The options of chmod are as follows:. + for adding and – for removing.
Give the file’s owner read and write permissions and only read permissions to group members and all other users:. If you want to set permissions on all files to a+r, and all directories to a+x, and do that recursively through the complete subdirectory tree, use:. To remove execute permissions from group and other (i.e from all users except the file's owner):.
$ chmod a+r file.pl Delete execute permission for all everyone (a):. Chmod command is followed by which level user i.e. To recursively operate on all files and directories under a given directory, use the chmod command with the -R, (--recursive) option.
The chmod command changes the access permissions of files and folders. The default umask is 022, or in other words it allows all permissions except write permissions to groups and others. Chmod references operator modes filename The references are shorthand (u, g, or o) for each class.
This is very insecure and dangerous action. Another way to use chmod is to provide the permissions you wish to give to the owner, group, and others as a three-digit number. To add the write permission to the username user.
Chmod command understanding how-to grant file permissions why i said title like that, because chmod command used for changing file mode bits. – Jaken551 Mar 10 '18 at 13:00. To change the permissions of a file, one uses the chmod command, with the following syntax:.
$ chmod u=rw,g. Both the codes give read (code=4) permission to user, write and execute (code=3) for group and read and execute (code=5) for others. Do not give full permissions.
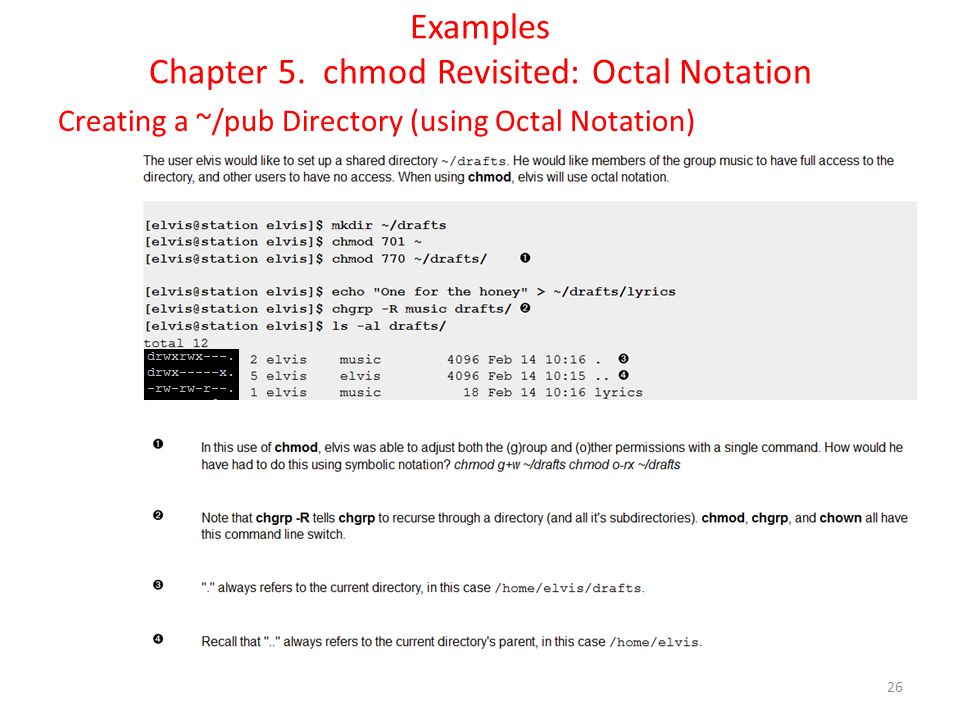
In other words, give read permission to user, group and others:. To add the write permission to the group. This command changes the mode of Fred's home directory (represented by the ~), giving permission to all users to get to files in that directory.
Read permission on a. The second case, I will leave you guys to figure out. The command that executes such tasks is the chmod command.
We will use 664binary permission. $ chmod -R g+rwx /var/www. You also want to add execute permission for the User owner.
Another useful permission is given other users read permission but denying from editing the file. Chmod a=r foldername to give only read permission for everyone. Chmod changes the permissions of each given fileaccording to mode, where modedescribes the permissions to modify.
To change directory permissions for everyone, use “u” for users, “g” for group, “o” for others, and “ugo” or “a” (for all). The general syntax to recursively change the file’s permissions is as follows:. Chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits.
Max OS-x specific, but still good, permissions;. G- group of users o,a - all u- own user So, in the above code chmod go-rwx,u+w file.sh --> revokes all permissions from group users, all and gives write permission for the own user. The chmod command, like other commands, can be executed from the command line or through a script file.
Chmod -R a+rwX directory/ as root. Use u for user, g for group, o for other, and a for all. If you need to list a file's permissions, use the ls command.
It means giving 755 permission to the all the files in recursive manner:. To change permissions recursively in all subdirectories below the specified directory, add the -R option;. We can give all permission to all roles which means user, group and others can read, write and execute.
Each shell script must have the execute permission. The letter or letters representing the owner (u), group (g), other (o) or all (a) followed by a + for adding permissions or a – for taking away permissions and then the letter for the permission (r for read, w for write and x for execute).In the above example, I added the execute permission for all users. Remember, the owner’s permissions always come first, then followed by group and others.
The middle digit represents the permissions for the group members. User, group, and all others. You can do all of it one single command:.
Modecan be specified with octal numbers or with letters. Chmod -R 755 myfiles. Chmod -R MODE DIRECTORY.
$ chmod a+rx pager.pl Next, sets read and write permission for user, sets read for group, and remove all access for others:. To add read, write permissions to user and group to the permissions that already exist:. For example, we can make our document read-only for every user and group with:.
Chmod 755 sets the 755 permission for a file. The resulting permissions would be like this:-rwxrwx--x 1 abhi itsfoss 457 Aug 10 11:55 agatha.txt. $ chmod a-x myscript.sh Adds read and execute permissions for everyone (a):.
755 means full permissions for the owner and read and execute. Chmod -R will change all the permissions of each file and folder under a specified directory at once. By - Linux tutorial - team.
And even this… chmod 775 file_name chmod ug+rwx,o=rx file_name Both the commands give all permissions (code=7) to user and group, read and execute (code=5) for others. $ chmod -R 600 /opt/lamp Read By Group But Not Edited. $ chmod 777 -R /path/to/Dir To assign reasonably secure permissions to files and folders/directories, it's common to give files a permission of 644 , and directories a 755 permission, using the find command and a pipe we can target just files.
We can combine references to set permissions all at once. N Description ls binary 0 No permissions at all --- 000 1 Only execute --x 001 2 Only write -w- 010 3 Write and execute -wx 011 4 Only read r-- 100 5 Read and execute r-x 101 6 Read and write rw- 110 7 Read, write, and execute rwx 111. Others can read only".
Chmod -R o+x mydir. Psftp> chmod go-rwx,u+w file.sh psftp> chmod a+r file.sh r- read w-write x-execute + symbol gives the permissions mentioned and - symbol revokes the permissions. We will set binary permission 660 for this.
It means giving 777 permission to the all the files in recursive manner:. Therefore, rwx is equal to 7. That looks like this:.
Let us understand the Permission system on Linux. User, group or all. To give permissions to all users, use chmod a+w testfile.txt.
Sudo usermod -a -G groupname username. Group members and other users can read and execute, but cannot write. To assign read, write permissions only for user and group:.
Mode can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new. Set the permissions of file.htm to "owner can read and write;. Chmod ugo+rwx foldername to give read, write, and execute to everyone.
To remove execute permissions for all:. It can change file system modes of files and directories. The use of an equal sign (=) wipes all previous permissions for that category.
User can read, write, and execute;. Often going through all of these steps isn't necessary, but this is a useful exercise to see how these commands work!.

Changing File Permissions Wordpress Org

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct
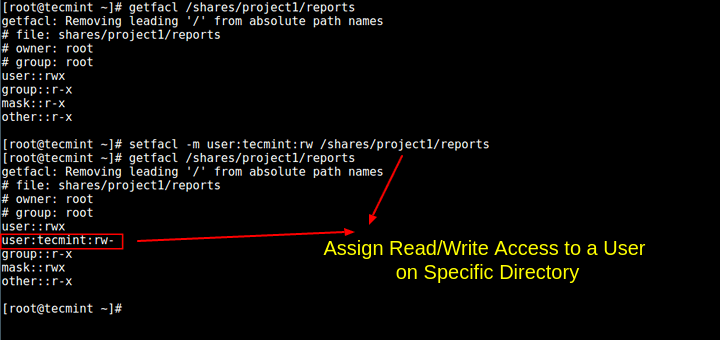
Assign Read Write Access To A User On Specific Directory In Linux

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support
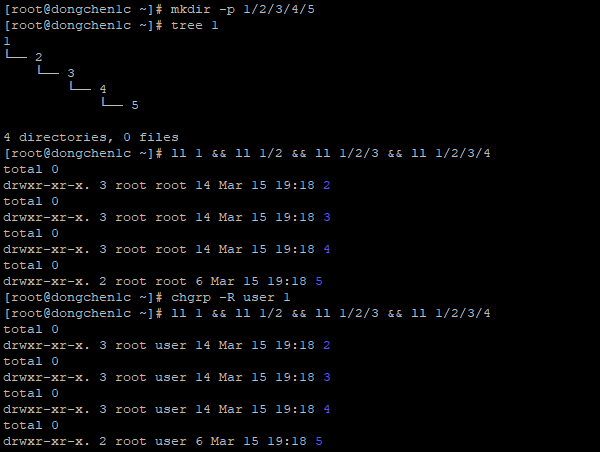
44 File Permissions Chown Chgrp Chmod Umask Dong A Place To Track My Time Log
Linux Chmod Tips
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq1nsq3kxri7ryrifobs2rfobawbv4hezfw9 Ldf4feblahyn09 Usqp Cau

Chmod Why It Matters User Permissions In Os X Droppedframe Com

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

Linux File Permission Javatpoint
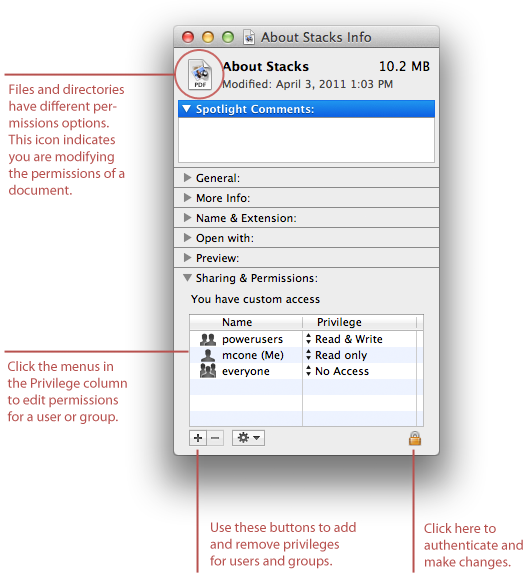
How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux

Linux Permissions An Introduction To Chmod Enable Sysadmin
Linux Privilege Escalation Using Suid Binaries

Give Write Access Chmod Command

Permissions In The Finder And Command Line The Eclectic Light Company
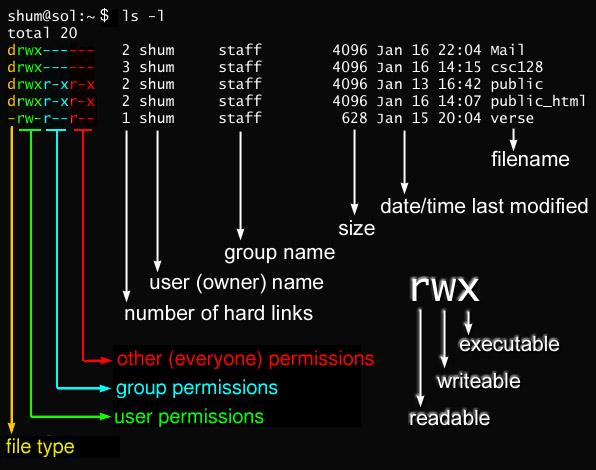
Javarevisited 10 Example Of Chmod Command In Unix Linux

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Lesson 9 Setting And Using Permissions Overview Describing File Permissions Using Execute Permissions With A File Changing File Permissions Using Mnemonics Ppt Download

Directory How Can I Change Permissions Of A Folder Including Its Enclosed Files And Subdirectories Ask Ubuntu

Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Youtube
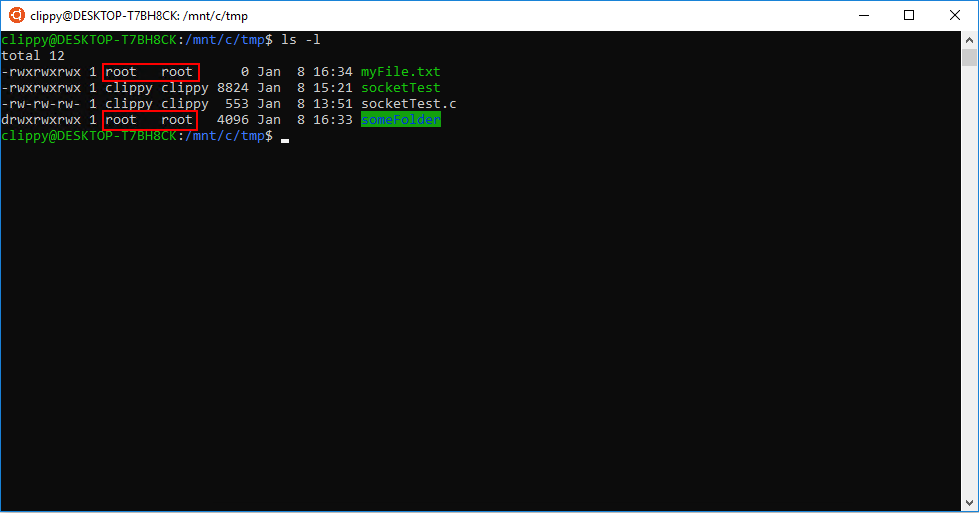
Chmod Chown Wsl Improvements Windows Command Line
Q Tbn 3aand9gctejwme2dmdomohoy140oy72qp3e1pn8jtuanchtus Usqp Cau

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Chmod Cheatsheet Linux

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Designlinux

Chmod 0400 Means
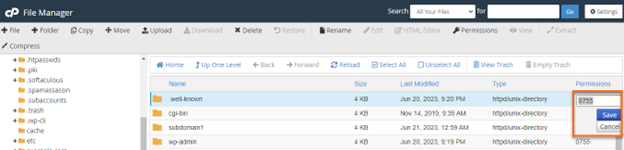
How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux Basic Linux Permission Linux File Permission Wiz Maverick Benisnous

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples
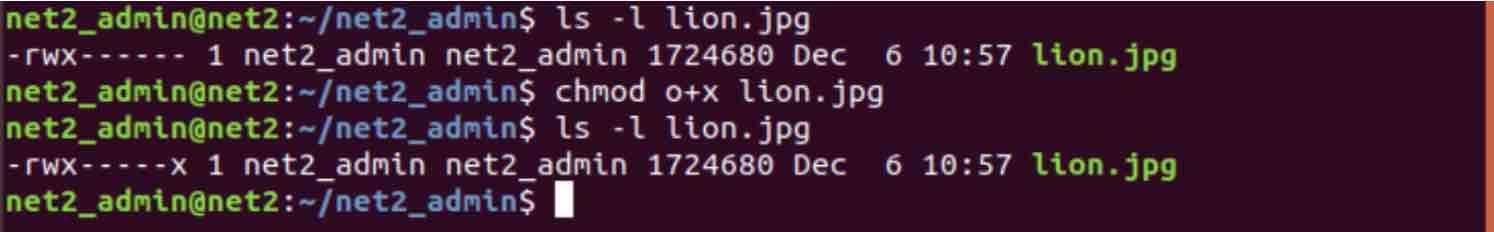
How To Manage Permissions In Linux Guide For Beginners
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu

What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro

Unix Linux Os X File Permissions

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

Linux File Permission Change By Chmod Command In Linux Guide For Beginners

Linux File Permissions Tutorial For Beginners
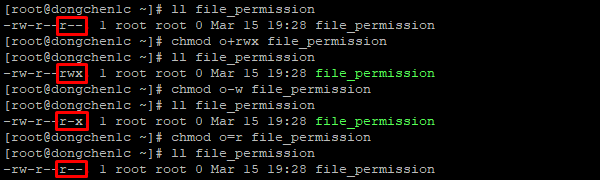
44 File Permissions Chown Chgrp Chmod Umask Dong A Place To Track My Time Log

Requisite Access Rights At Server

Xampp Htdocs Permission Issue And Fix In Ubuntu

Linux Chapter 3 Permission Management Commands Change File Permissions Chmod 777 Root A Programmer Sought

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission

Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Kirelos Blog
Q Tbn 3aand9gcr2lfpzbutqythmvbwafnxvyggqfj7hnw6fhh Kcozkk8m5 V7o Usqp Cau
/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)
Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights

Change File And Folder Permission On Ubuntu Chmod Chown Command In Linux Youtube

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Linux Chmod Command Tutorial With Examples To Change Permission Of Files And Folders Poftut

How To Change Permissions And Owners Via Linux Command Line

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

Unix File Permissions Computer Science

Setting File And Directory Permissions Computational And Information Systems Laboratory
K Yp7az Gi B4m

Setup Correct Files And Folders Access Permissions Efficiently Web Site Scripts Com

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World
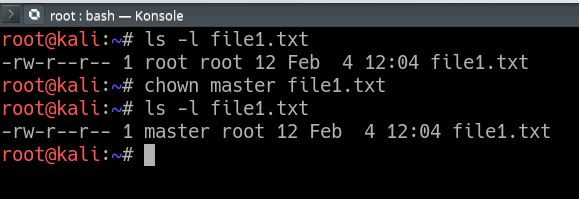
Chown Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
Chmod Jessica Peng

How Do Linux File Permissions Work
Why Would Using Chmod 777 Recursively From The Root Cause A Linux Box To Not Boot I Could Understand This If I Were Limiting Permissions But Why Would Adding Permissions Cause This

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode

Understanding File Permissions

Give Write Access Chmod Unix

Understanding Linux File Permissions With Chmod Umask Chown And Chgrp Liquidon Net
Chmod 0400 Means

Linux Commands 5 File Permission Chmod Youtube

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command Nixcraft

Chmod Wikipedia

Ownership And Permissions
Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Ppt Video Online Download
How To Deny File Permissions To Everyone Except Yourself In Linux Linuxhostsupport

Understanding Basic File Permissions And Ownership In Linux The Geek Diary

Linux File Permission Change By Chmod Command In Linux Guide For Beginners

Change Ownership And Rights To Files And Folders In Linux Smashing Lab

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier

Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq6mtqrr2tbkvj8mt7j61itbsugnnfl3ltc9cdgqfgdswx0kkor Usqp Cau

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight
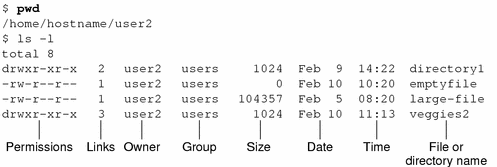
File And Directory Security Solaris Advanced User S Guide

8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut
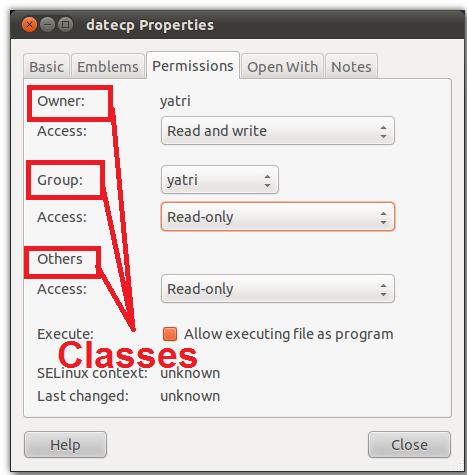
What Is Chmod 777

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected

Linux Users And Groups Linode



