Chmod

14 Permission And Modification Times

Chmod X Windows Nativeyellow
Why Would Using Chmod 777 Recursively From The Root Cause A Linux Box To Not Boot I Could Understand This If I Were Limiting Permissions But Why Would Adding Permissions Cause This

Chmod X Chmod

8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials
If you have any questions or feedback, feel free to leave a comment.
Chmod. Right now it has effect only under Unix or NonStop Kernel (Tandem). This is not a problem since the permissions of symbolic links are never used. The request is filtered by the umask.
Chmod +hrs sysfile sets the hidden, read-only, and system attributes for sysfile. Hopefully, this article can help you understand better about the file permissions in Unix system and the origin of the magical number “777”. Please note the warning in the chmod with sudo section and the Warning with Recursive chmod section.
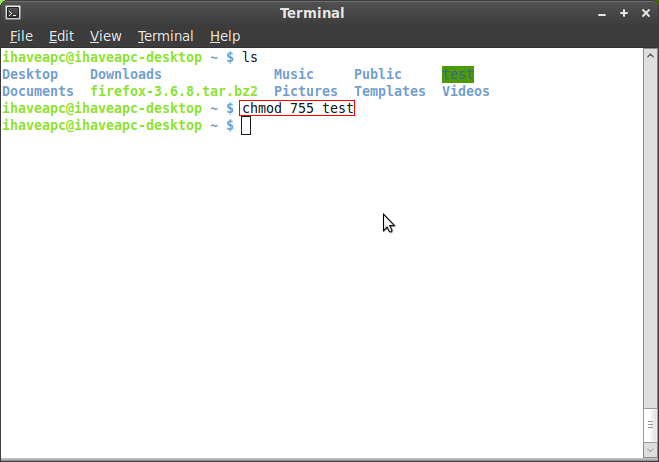
Chmod +x filename.shto make filename.sh executable. To view these online, enter. $ chmod u+x filename 2.
Chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits. The chmod command is used to change the various permission bits of a file or directory. To give write permissions to everyone, execute:.
The chmod command changes the access mode of one file or multiple files. The all (a) mode is the same as ugo, allowing the previous command to be. This is done with the chmod command.
The chmod system call cannot change their permissions. Change permission for all roles on a file/directory. In Unix and Unix-like operating systems, chmod is the command and system call which is used to change the access permissions of file system objects (files and directories).
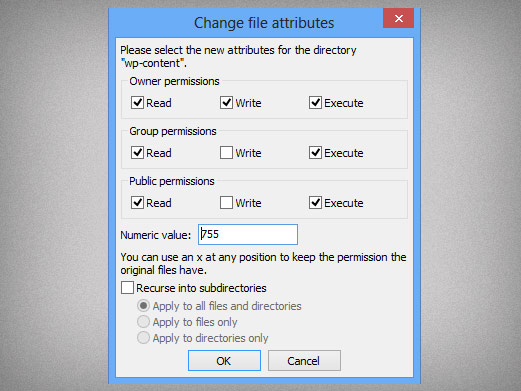
To change the permissions of a directory, we run:. Following example removes read and write permission for the user. Chmod means ‘change mode’ and it changes file or directory mode bits (the way a file can be accessed).
Chmod file has metadata. Chmod never changes the permissions of symbolic links;. This ensures that only authorized users and processes can access files and directories.
Chmod Modifies File Permissions In Linux, who can do what to a file or directory is controlled through sets of permissions. One set for the owner of the file, another set for the members of the file’s group, and a final set for everyone else. Chmod stands for “ Change Mode ” and is used to modify the permissions of files and directories in a Linux based system.
Chmod +x or chmod a+x ('all plus executable bit') makes the file executable by everyone. If you need to change a file permission, use the chmod command. You can change file permissions in this format:.
Mykyta Dolmatov / Getty Images. The name is an abbreviation of change mode. On Unix-like operating systems, a set of flags associated with each file determines who can access that file, and how they can access it.
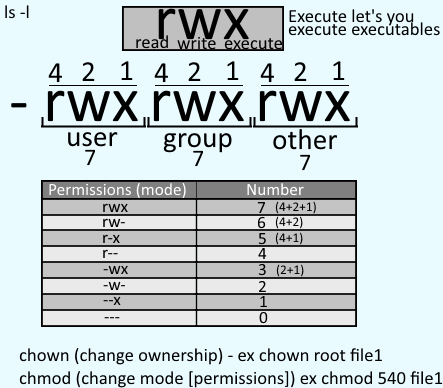
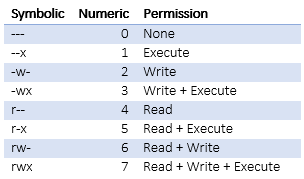
In short, “chmod 777” means making the file readable, writable and executable by everyone. In Linux, access to the files is managed through the file permissions, attributes, and ownership. The first element of the list must be the numeric mode, which should probably be an octal number, and which definitely should not be a string of octal digits:.
There's no way to set the permissions for files automatically in only this directory that are created after you set the permissions, but you could change your system-wide default file permissions with by setting umask 022. To put it simply, use chmod command to change the file or directory permissions. If you do this to a directory, it makes the directory searchable, instead.
I’ll also explain some the popular terms like chmod 777 or chmod 755 or chmod -r. Using letters is easier to understand for most people. Additional restrictions may cause the set-user-ID and set-group-ID bits of MODE or RFILE to be ignored.
One component can be computed by adding up the needed permissions for that target user base. Umask is a 3 digit octal number. To recursively set permissions of files based on their type, use chmod in combination with the find command.
Chmod never changes the permissions of symbolic links, since the chmod system call cannot change their permissions. Using symbolic modes (letters to indicate the categories and permission). Recursive chmod with -R and sudo.
You can use chmod in the command line to change file or directory permissions on unix or unix-like systems such as linux or BSD. How‐ ever, for each symbolic link listed on the command line, chmod changes the permissions of the pointed-to file. To remove the write permission for all other users, we run:.
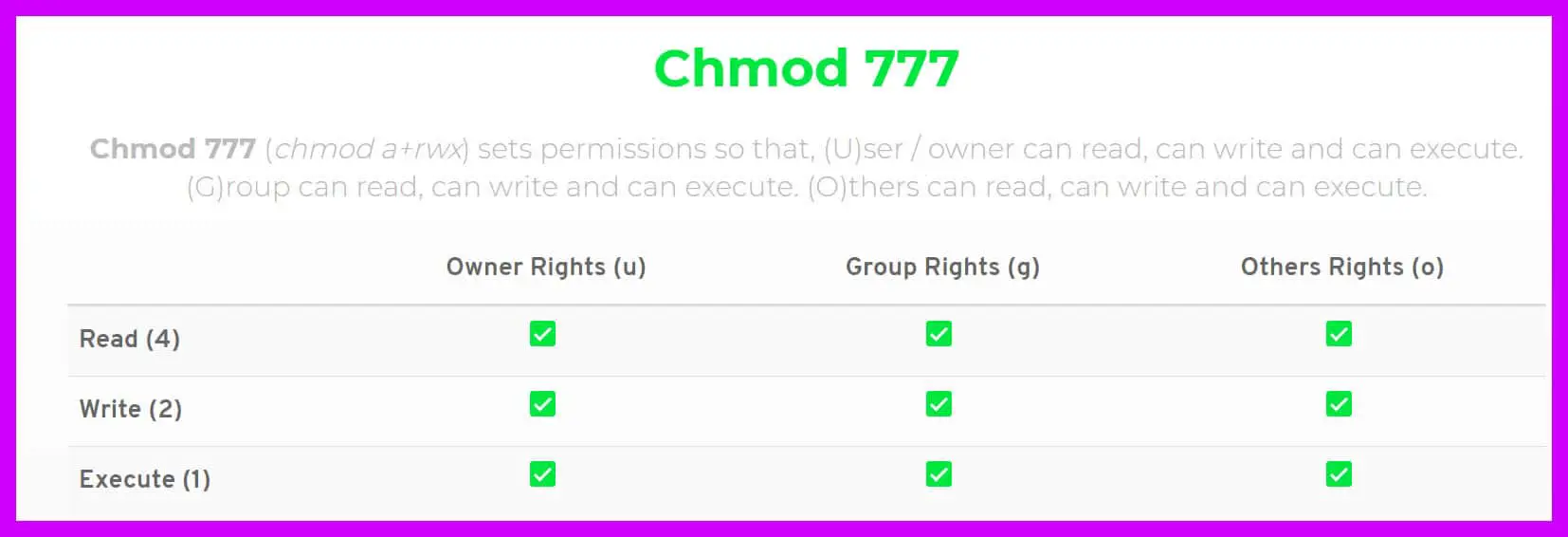
The name is an abbreviation of change mode. Chmod 777 Chmod 777 (chmod a+rwx) sets permissions so that, (U)ser / owner can read, can write and can execute. To remove the write permission for others for file2:.
The calling process does not have appropriate privileges, that is, superuser authority (UID=0). $ chmod a+rx pager.pl Next, sets read and write permission for user, sets read for group, and remove all access for others:. To change the permissions of multiple files and directories with one command.
See the section on directory based tasks, on how the inclusion/exclusion of files works, and how to. $ chmod u=rw,g=r,o= birthday.cgi In this file example, sets read and write permissions for user and group:. For example, to explicitly make file3 readable and executable to everyone:.
(O)thers can read, can write and can execute. $ chmod ug=rw /var/www/html/data.php. Chmod u+x will made the file executable for your user (it will only add it for your user, though it may be already executable by the group owner, or "other").
Can the script only read the info, or can it write information as into it as well. The permissions are also UNIX style, like the argument for the chmod command. In this method, the chmod command takes flags or symbols which represent the owner, group, others or all users ( u, g , and o) in the syntax.
CHMOD is listed in the World's largest and most authoritative dictionary database of abbreviations and acronyms The Free Dictionary. Chmod file does not have metadata (default) Chmod will only have one effect, if you remove all the write attributes of a file then the 'read only' attribute on the Windows file will be set, since this is the same behaviour as CIFS (Common Internet File System) which is the SMB (Server Message Block) client in Linux. 755 can be separated as.
They are list of letters that specifies whom to give permissions. In this article, I’ll share with you some of the practical examples of chmod command. Modecan be specified with octal numbers or with letters.
Returns the number of files successfully changed. Chmod is Linux command used to change file permissions.chmod changes user, group and other read, write and execute permission.chmod 755 is popular use case for chmod .chmod 755 is generally used to make most of the operations without problem because it provides ease for system administrators while running applications. This tutorial covers how to use the chmod command to change the access permissions of files and directories.
These flags are called file permissions or modes, as in "mode of access." The command name chmod stands for "change mode." It restricts the way a file can be accessed. In Unix-like operating systems, the chmod command is used to change the access mode of a file. You can combine multiple references and modes to set the desired access all at once.
Use comma to separate the multiple permission sets as shown below. $ chmod u+r,g+x filename 3. The group ID of the file does not match the group ID or supplementary group IDs of the calling process.
Introduction Multi-user systems, such as Linux, require setting up and managing file permissions that ensure only authorized users have access to files they are supposed to. Chmod --reference= source-file destination file In the above command, source-file is the file whose permission bits you want to copy, and destination-file is the file whose permission bits you want to change. Chmod stands for change mode, which changes the file or directory mode bits.
The chmod command changes the access permissions of files and folders. Chmod a=rwx file turns on read, write, and execute permissions, and turns off the hidden, archive, and system attributes. Add multiple permission to a file/directory.
Chmod changes the permissions of each given fileaccording to mode, where modedescribes the permissions to modify. Description chmod changes the access permissions, or modes, of the specified file or directory. There are three sets of permissions.
Sudo usermod -a -G groupname username and then execute. * fchmod() changes the permissions of the file referred to by the open file descriptor fd. Another way of assigning permissions is by using the text notation.
By using this command, we can set the read, write, and execute permissions for all three of the permission groups (Owner, Group and Other) in Linux. Chmod() automatically clears the S_ISGID bit in the file's mode bits if all these conditions are true:. In contrast, chmod ignores symbolic links encountered during recursive directory traversals.
In the terminal, the command to use to change file permission is chmod. Chmod - What is it?. For more information, including octal specification of permissions, refer to the Unix User's Manual pages for chmod(1) and ls(1).
Chmod changes the permissions of each given file according to mode, which can be either an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new permissions or a symbolic representation of changes to make, (+-= rwxXstugoa). There are two ways to represent the MODE:. Chmod LIST Changes the permissions of a list of files.
Chmod 775 / path / to / file. The chmod command with the -R options allows you to recursively change the file’s permissions. 0644 is okay, but "0644" is not.
Chmod() changes the permissions of the file specified whose pathname is given in path, which is dereferenced if it is a symbolic link. $ chmod 755 -R directory_name $ chmod 755 -R /home/linuxtechi/data Example 3) Assign permissions using text notation. $ chmod a-x myscript.sh Adds read and execute permissions for everyone (a):.
(Modes determine who can read, write, or search a directory or file.) Users with read access to SUPERUSER.FILESYS.CHANGEPERMS (a UNIXPRIV class profile), can use the chmod command to change the permission bits of any file. EXAMPLES chmod -w nowrite makes file nowrite read-only. Chmod clears the set-group-ID bit of a regular file if the file's group ID does not match the user's effective group ID or one of the user's supplementary group IDs, unless the user has appropriate privileges.
However, for each symbolic link listed on the command line, chmod changes the permissions of the pointed-to file. $ chmod u-rx filename 4. The chmod command, like other commands, can be executed from the command line or through a script file.
Chmod - Unix, Linux Command - chmod - To change access permissions, change mode. Sooner or later in the Linux world, you will have to change the permission on a file or directory. With great power comes great responsibility, and there’s no denying that the chmod command is an extensive and powerful.
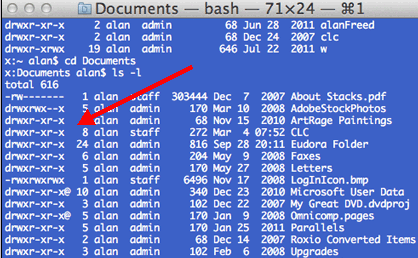
Remove permission from a file/directory. Looking for online definition of CHMOD or what CHMOD stands for?. Following is a sample of ls -l command output.
Sudo chmod g+w myfolder to add the write permission to the group. This would grant all users and user groups with read and write access to your file, as well as allow all users to execute the file. (G)roup can read, can write and can execute.
Sudo chmod u+w myfolder to add the write permission to the username user. The references are used to distinguish the users to whom the permissions apply i.e. The command takes the general form:.
This is not a prob‐ lem since the permissions of symbolic links are never used. To change all the permissions of each file and folder under a specified directory at once, use sudo chmod with -R. Chmod stands for Change Mode and is a command often needed for installing scripts (CGI, PHP etc.) on a UNIX server, after uploading the file (with FTP) you may need to change the permissions.Basically it tells the server who can make what changes to the file or folder, i.e.
What does chmod mean?. How to use chmod?. But if you want to add this user to the group associated with "myfolder", you can run.
The chmod() function changes permissions of the specified file. Changes the permissions of a file or all files inside specified directories. I.e., you can list the contents of a directory that you have +x.
The mode parameter consists of three octal number components specifying access restrictions for the owner, the user group in which the owner is in, and to everybody else in this order. If you need to list a file's permissions, use the ls command. Chmod permission directory name To change the permissions of a directory with its files and sub-directories recursively.
Man chmod man ls A variable called `umask' is used as a permission mask for all newly created files and directories. From one to four octal digits Any omitted digits are assumed to be leading zeros.

When Sudo Chmod 755 Library Tomcat9 Bin Sh Occurred An Error Stack Overflow

Understanding Linux File Permissions With Chmod Umask Chown And Chgrp Liquidon Net
Chmod Chown Wsl Improvements Windows Command Line

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Linux File Permission Javatpoint

How Did The Number 777 In Chmod 777 Come Out Under Linux Laptrinhx
Solved This Is In Linux While Logged In As A Regular Use Chegg Com

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux

Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux
What Is Chmod 777

What Did We Do When We Were Chmod 777 Develop Paper
Linux Command Line Basics Part 4 I Have A Pc I Have A Pc

Linux File Permissions Know The Reason Behind That Chmod 777 By Abhishek Chandra Medium

Linux Commands 5 File Permission Chmod Youtube

Unix Permissions The Easy Way Index Of All Chmod Permutations By Semi Koen Sep Towards Data Science

This Chmod Calculator Makes Creating Chmod Commands A Cakewalk Hongkiat

Chmod Wiki Ask Ubuntu

Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples

Devrant A Fun Community For Developers To Connect Over Code Tech Life As A Programmer

Xampp On Windows 7 Set Chmod Stack Overflow

Extropia Tutorials Introduction To Unix For Web Technicians The Chmod Utility

Chmod Command Tutorial How To Recursively Set Permissions In Sub Folders

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Chmod Umask Stat Fileperms And File Permissions

How To Add Chmod X On A File From Right Click Menu Service In Mac Super User

Chmod 777 Allocating The Least By Amith Jayasekara Medium

Chmod Not Working Q A Dataquest Community

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices
What Is Chmod How To Use Chmod For Wordpress File Permissions

14 04 Chmod Not Working In A Non Super User Ask Ubuntu
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs Trmaopb41lzfo2wl Mi6olorurkywaddbudhnw Ne1mor3ct Usqp Cau
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq6mtqrr2tbkvj8mt7j61itbsugnnfl3ltc9cdgqfgdswx0kkor Usqp Cau

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

Use Of Chmod Command In Linux Devopsdex

How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission

Explaining The Difference Chmod X And Chmod A X Youtube

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode

How To Use Chmod Change Mode Repair Your Pc Now

Chmod 777 Comic Dzone Security

This Chmod Calculator Makes Creating Chmod Commands A Cakewalk Hongkiat

Linux Chmod Command Clearly Explained Codedodle

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux

Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech

Permissions Reverting From Executing Chmod By Mistake Ask Ubuntu

Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube

Chmod 7777

Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples

Linux File Permissions Tutorial For Beginners

Chmod Command In Unix Unix File Permissions Chmod With Examples Chwn Command Chgrp Command Unmask

Chmod Wikipedia
Freekb Linux Commands Chmod Change A File Or Directory Standard Permissions
Q Tbn 3aand9gcr9rnnth31jdnr94db Zmbdt5bh907clokeeor9me5yqbuufaiw Usqp Cau

Title Of Folders With Chmod 777 Is Not Readable Issue 36 Hukl Smyck Color Scheme Github

Chown Chmod

Csc128 Permissions And Links Chmod And Ls

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

How To Use The Chmod Command 2 Minute Linux Tips Network World

Chmod 755 Livecoding Foxdot Python Youtube

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Chmod Permissions Yaman S Website

Chmod Command Vichhaiy Welcome

Permissions How Can I Restore The Executable Bit Of Bin Chmod Ask Ubuntu

What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu

Chmod Command

Chmod Unix Article About Chmod Unix By The Free Dictionary

Numeric Permissions Table Linux Chmod Command Linux Permissions

Common Bash Commands
Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq1nsq3kxri7ryrifobs2rfobawbv4hezfw9 Ldf4feblahyn09 Usqp Cau

Chmod 755 Command What Does It Do Codefather

When Sudo Chmod 755 Library Tomcat9 Bin Sh Occurred An Error Stack Overflow
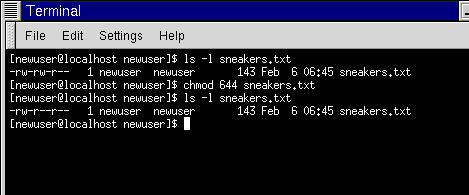
Fun With Numbers In Chmod

Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Youtube
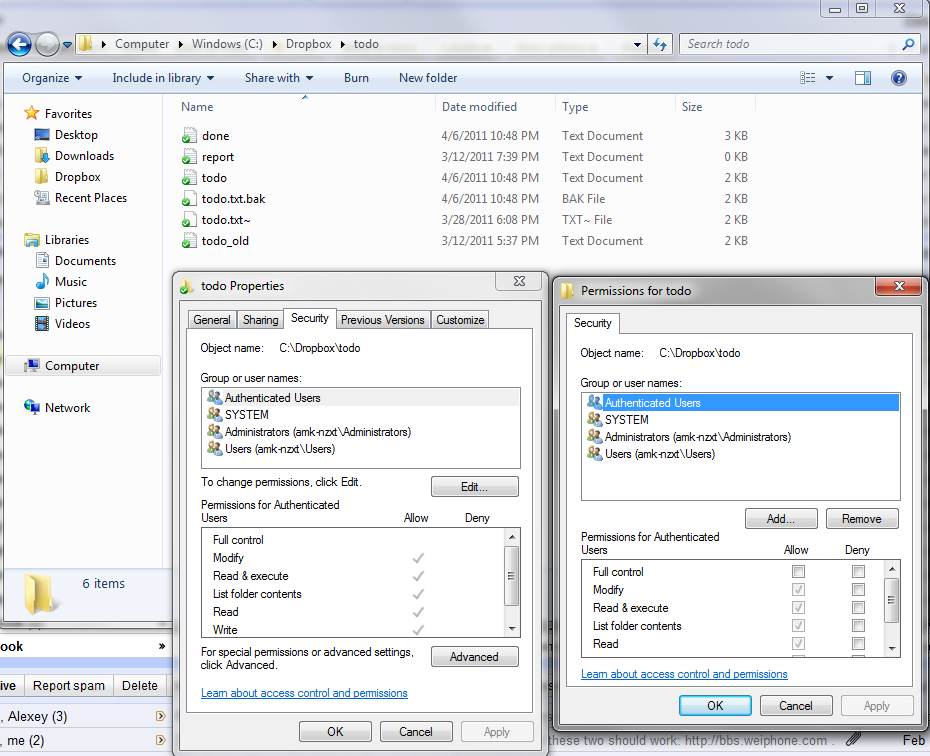
Permission Denied For Chmod Cygwin On Windows 7 Doesn T Play Nice With Files In Dropbox

Explain Absolute And Relative Permission Using Chmod Linuxteach

Linux File Permissions And Chmod Doug Vitale Tech Blog

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)
Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights

Chmod Cheatsheet Linux

Linux File Permission Change By Chmod Command In Linux Guide For Beginners

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux Basic Linux Permission Linux File Permission Wiz Maverick Benisnous

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Ownership And Permissions

Pdf Chmod Cheat Sheet Sunny Yiu
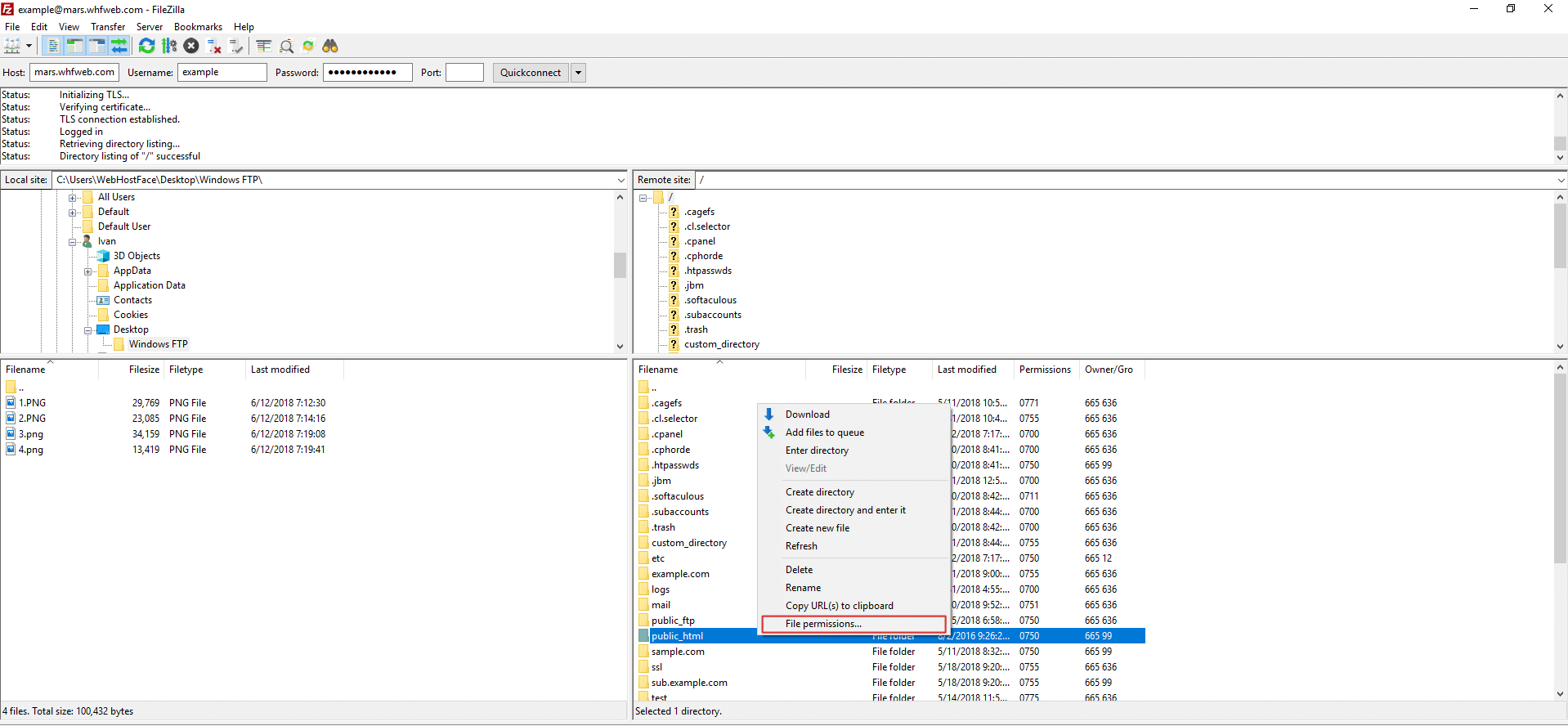
Change Ftp Permissions With Filezilla On Windows Computer
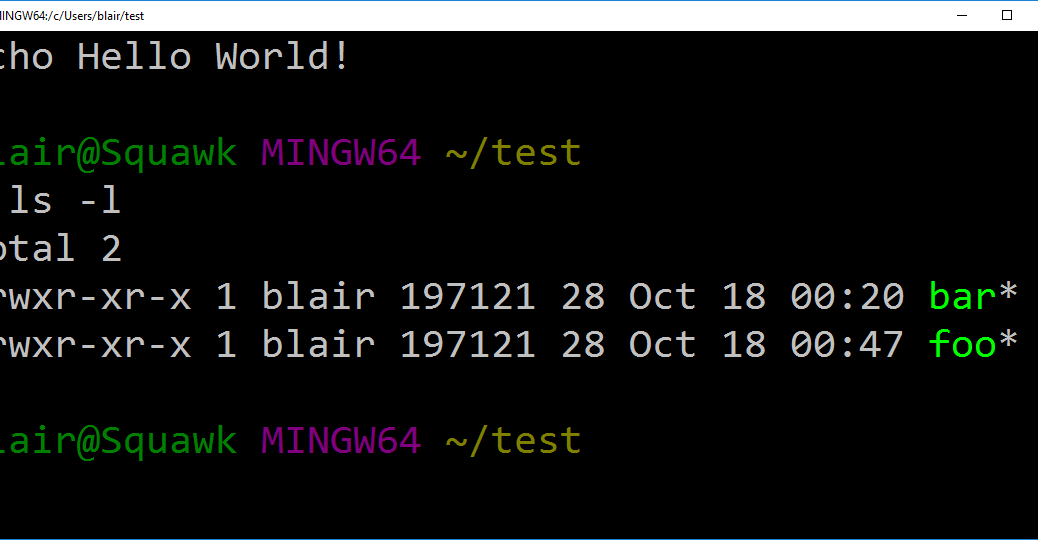
Problem Chmod Is Ignored In The Git Bash Prompt Chaos And Penguins

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint
Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions

Command Line I Can T Change Mode For Some Directories Using Chmod Ask Ubuntu

Chmod Wiki Ask Ubuntu

Chmod Command In Unix Learn Unix Online Fresh2refresh Com

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks



