Chmod Give All Permissions

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod
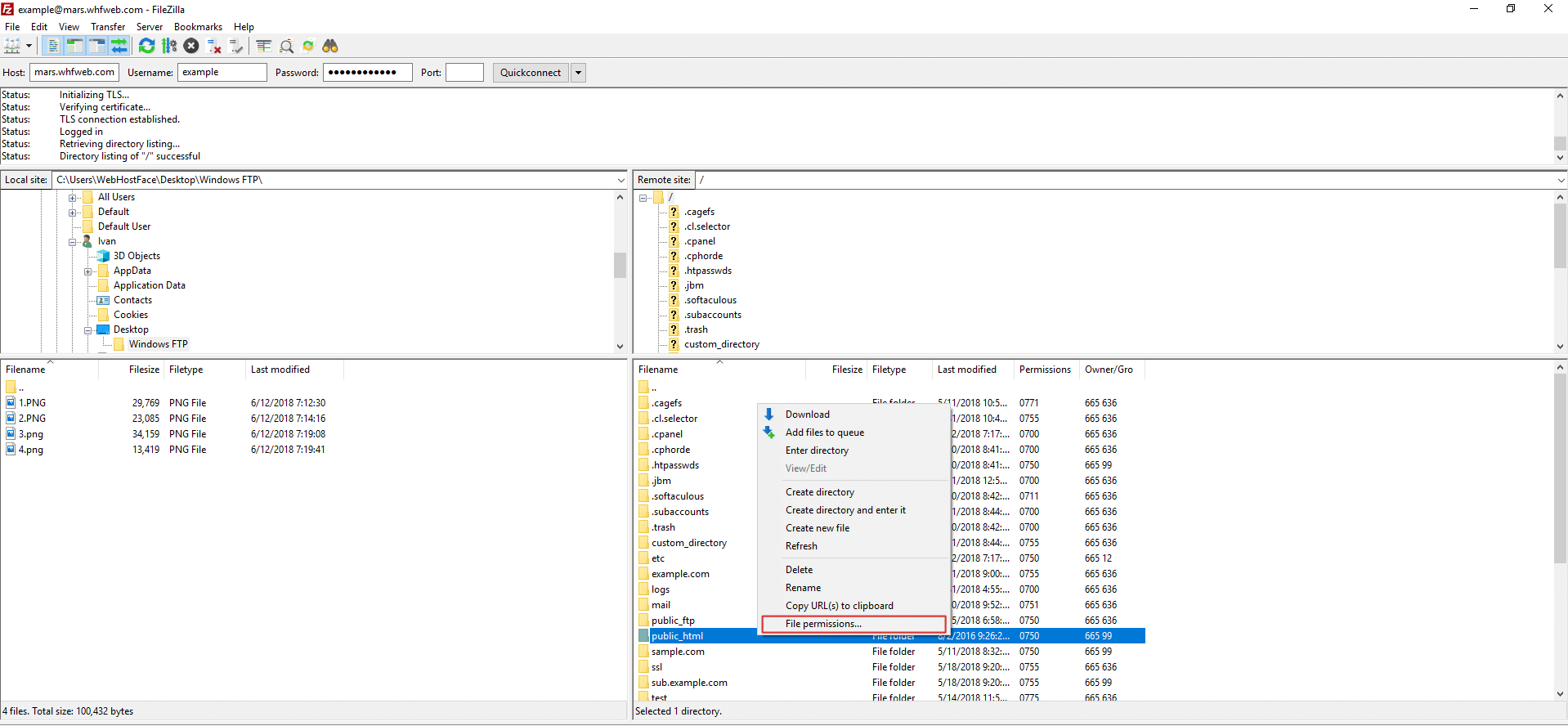
Change Ftp Permissions With Filezilla On Windows Computer

How To Set Access Rights For Files And Folders With Chmod

Setting File And Directory Permissions Computational And Information Systems Laboratory

Setup Correct Files And Folders Access Permissions Efficiently Web Site Scripts Com

Linux Permissions An Introduction To Chmod Enable Sysadmin
For help, see List the files in a directory in Unix.

Chmod give all permissions. For example, to use chmod to set permissions of file "filename" to -rwxrwxrwx you could run:. Sudo chmod 777 filename = I don't know the file name;. Read permission on a directory gives you the ability to lists its content.
Add other options as desired;. If you want to set permissions on all files to a+r, and all directories to a+x, and do that recursively through the complete subdirectory tree, use:. We overwrite the current permissions).
Every file and directory in your UNIX/Linux system has following 3 permissions defined for all the 3 owners discussed above. It can change file system modes of files and directories. To make file readable, writable and executable by everyone.
First, modify ACL of a chmod binary file for user with read and execute permissions:. To give the owner all permissions and world read and execute you would type chmod 705 filename. We can restore chmod executable permissions using "setfacl" command.
Mode can be specified with octal numbers or with letters. The second way to modify permissions with the chmod command is to use a number to specify each set of permissions for the file. Chmod 700 filename You can do the same in symbolic mode.
Chmod 775 /path/to/file chmod command uses & Explanation. User - What the owner of the file can do. In Linux, files and directories are treated similarly.
This would grant all users and user groups with read and write access to your file, as well as allow all users to execute the file. For our example command, we are going to give the group permission group, read and write privileges on a file called readandwrite. To change directory permissions for everyone, use “u” for users, “g” for group, “o” for others, and “ugo” or “a” (for all).
My sd card in my usb card reader will not allow me to add files while in ext4. There are three sets of permissions to worry about with any directory/file:. You can set all files in a folder or directory to writeable with chmod -R 775 directory.
Correspondingly, users have a username (unique to each user). The chmod command specifies which class or classes (user, group, other) have access to the. There are three sets of permissions.
The chmod command (change mode) is a shell command in Linux. The command that executes such tasks is the chmod command. # chmod +x $(which chmod) Finally, remove all ACL entries of chmod.
Chmod changes the permissions of each given file according to mode, where mode describes the permissions to modify. The chmod command changes the access permissions of files and folders. View (u)ser, (g)roup and (o)thers permissions for chmod 644 (chmod a+rwx,u-x,g-wx,o-wx) or use free online chmod calculator to modify permissions easily.
Use sudo, the find command, and a pipemill to chmod as in the following examples. To recursively operate on all files and directories under a given directory, use the chmod command with the -R, (--recursive) option. Chmod Command in Linux Linux File Permission Introduction to Linux File Permission.
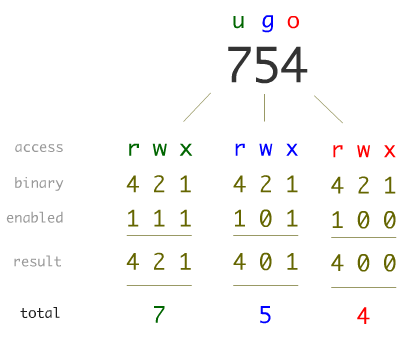
After user level we have provide what needs to be done i.e. Meanwhile, since group and others are only allowed to read the file, we give them 4. That’s why we enter 744.
To give the User group read and write permission, you would add up 4+2 to get 6. To give the owner all permissions and world execute you would type chmod 701 filename. Chmod -R a+rX * click below button to copy the code.
So, if you want to give a file 664 permissions, you’d issue the chmod command like this:. For example, if you want the owner to have all the permissions and no permissions for the group and public, you need to set the permission 700 in absolute mode:. Linux File Permission :.
In each group, the first character is for read access ( r ), followed by write access ( w) and the right to execute ( x ). Group - What users of the same group can do. Other - What anyone else can do.
The second case, I will leave you guys to figure out. In the following example, g is group bit, o is the 'other users' bit and the -sign is removing all permissions (rwx):. The absolute mode functions like the exclusive permission of the symbolic mode in that it exclusively sets the permission specified removing all other.
Avoid using boundary cases, such as chmod 777 <file-name> and chmod 000 <filename>. You can combine multiple references and modes to set the desired access all at once. Using symbols (alphanumerical characters) using the octal notation method.
We’ll wrap up with a bit of extra advice related to chmod:. Both the codes give read (code=4) permission to user, write and execute (code=3) for group and read and execute (code=5) for others. The modes include permissions and special modes.
Let us understand the Permission system on Linux. The general syntax to recursively change the file’s permissions is as follows:. Chmod ugo+rwx foldername to give read, write, and execute to everyone.
By - Linux tutorial - team. Mykyta Dolmatov / Getty Images. Here are some examples of how to use the chmod command in numeric mode:.
Recursive chmod using find, pipemill, and sudo To assign reasonably secure permissions to files and folders/directories, it's common to give files a permission of 644, and directories a 755 permission, since chmod -R assigns to both. Each shell script must have the execute permission. # setfacl -m u::rx /usr/bin/chmod.
Remember that you need read permissions in order to list directories and subdirectories. Adds write permission to the directory docs and all its contents (i.e. Linux file permission is a very important aspects in terms of security issues for the system administrator of Linux Operating System.
Chmod -R MODE DIRECTORY. Chmod command is followed by which level user i.e. The numerical equivalent is now:.
A = all + = add permissions - = remove permissions r = read w = write x = execute t = sticky bit so to add read permissiones for people in the files group I would do chmod g+r file. Chmod -R u+w,go-w docs:. The all (a) mode is the same as ugo, allowing the previous command to be expressed as:.
CHMOD Calculator Chmod 644. The permissions control the actions that can be performed on the file or directory. If you provide same permissions to directory you can enter into directory but you can’t do anything, directory execute permissions means providing the access to enter into directory.
User, group or all. Chmod Modifies File Permissions. So if you want to give all permissions (rwx) to a user, we need to add read (4), write (2), and execute (1).
Here are the other combinations you can have:. Recursively) for owner, and removes write permission for group and others chmod ug=rw groupAgreements.txt:. This permission give you the authority to open and read a file.
Actually, chmod Command in Linux plays a greater role to keep all the files and directories of the system safe and secure so that no unauthorized person. Each permission is assigned a value, as the following table shows, and the total of each set of permissions provides a number for that set. With great power comes great responsibility, and there’s no denying that the chmod command is an extensive and powerful tool to change file permissions on Mac.
The permission scheme described above also applies to directories. The basic syntax is:. You only want Others to have read permissions, so they get 4.
To remove the write permission for others for file2:. Chmod +x filename.sh to make filename.sh executable. A Few Additional chmod Tips.
Chmod is command which changes permission of a file or folder for particular user or group as per instructions provided. To view the permissions for all files in a directory, use the lscommand with the -laoptions. It stands for change mode.
I'm hoping if I change the permissions to non-root, it will let me add files. If no options are specified, chmod modifies the permissions of the file specified by file name to the permissions specified by permissions. As all Linux users, you will at some point need to modify the permission settings of a file/directory.
Changing permissions with chmod. Chmod -R will change all the permissions of each file and folder under a specified directory at once. Therefore, full permissions for everyone on the system would look like:.
Sets read and write permissions for user and Group:. If you need to list a file's permissions, use the ls command. Therefore, rwx is equal to 7.
Remember, the owner’s permissions always come first, then followed by group and others. As you can see, we start by first specifying the group permission group by utilizing the g letter. Give the file’s owner read and write permissions and only read permissions to group members and all other users:.
No such file or directory. In Linux, who can do what to a file or directory is controlled through sets of permissions. By setting permissions, you are replacing all existing permissions with the ones specified.
Chmod permission file_name There are two ways to define permission:. How to Change Groups of Files and Directories in Linux. The chmod command allows you to change the permissions of files using symbolic or numeric mode.
So chmod 744 script.sh would give us the exact same permissions that we just observed on script.sh:-rwxr–r– Where the user has all permissions ( read, write, execute), and the group and other both only have read permissions. The other way is terminal , where you can change the permission via Chmod. It can be used for individual files or it can be run recursively with the -R option to change permissions for all of the subdirectories and files within a directory.
$ chmod 777 -R /path/to/Dir To assign reasonably secure permissions to files and folders/directories, it's common to give files a permission of 644 , and directories a 755 permission, using the find command and a pipe we can target just files. For a directory, whoever has `read'. Server$ chmod go-rwx file.txt The file named script.cgi is now executable by the user and group.
Read, write and execute:. Chmod 111 techtutorial Execute permissions to all. Accessing files in the Linux root file system from Linux Any files created, modified, or accessed in the Linux root file system follow standard Linux conventions, such as applying the umask to a newly created file.
A dash means that the permission is turned off. For the Group, you need the same permissions, so they get the same number. 111 numerical value will grant execute permissions to user (owner), group and others to specified file.
To determine the mode (or permission settings) of a particular file, use the command `ls -lg filename'. For example, if you enter:. Sets read and write permissions for user and Group, and provides read.
If you use chmod 777 that means you assigned all the permissions i.e. Give the file’s owner read, write and execute permissions, read and execute permissions to group members. Chmod a=r foldername to give only read permission for everyone.
How to Set File Permissions Using `chmod' Files. To modify the permission flags on existing files and directories, use the chmod command ("change mode"). One set for the owner of the file, another set for the members of the file’s group, and a final set for everyone else.
Breaking this down, the a means all and rwx means set read, write, and execute. Mode can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new. Chmod is a command to change permission of a file.
For example, to explicitly make file3 readable and executable to everyone:. Using letters is easier to understand for most people. The chmod command, like other commands, can be executed from the command line or through a script file.
Using chmod 777 <file-name> gives everyone rwx permissions, and it is generally not a good practice to give full powers to all the users in a system. + for adding and – for removing. Permissions defines the permissions for the owner of the file (the "user"), members of the group who owns the file (the "group"), and anyone else ("others").
# Permission rwx Binary;. View (u)ser, (g)roup and (o)thers permissions for chmod 766 (chmod a+rwx,g-x,o-x) or use free online chmod calculator to modify permissions easily. Then, restore chmod permissions back to its original ones:.
And even this… chmod 775 file_name chmod ug+rwx,o=rx file_name Both the commands give all permissions (code=7) to user and group, read and execute (code=5) for others. I checked permissions and it's in root. Using chmod with Absolute Permissions.
I put in the random numbers/ letters assigned to it, but get error:.
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs J72hjomdluhqe6xjivy M6yrjmkqx9x3z3ps Rpnb8by3w7z Usqp Cau

Linux Commands 5 File Permission Chmod Youtube

Give Write Access Chmod 775
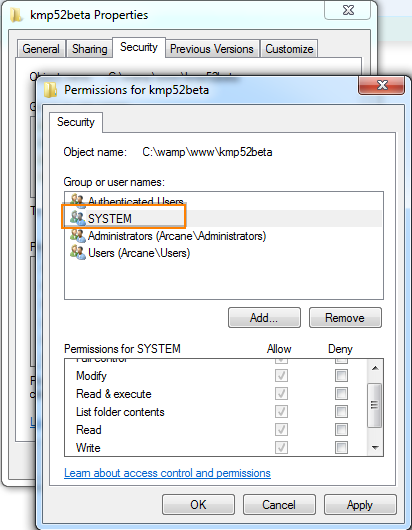
Setup Correct Files And Folders Access Permissions Efficiently Web Site Scripts Com

Give Write Access Chmod Command

Use Of Chmod Command In Linux Devopsdex

Use Of Chmod Command In Linux Devopsdex

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint

Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Youtube

Linux File Permissions Know The Reason Behind That Chmod 777 By Abhishek Chandra Medium
Q Tbn 3aand9gcr9rnnth31jdnr94db Zmbdt5bh907clokeeor9me5yqbuufaiw Usqp Cau

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux

8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut
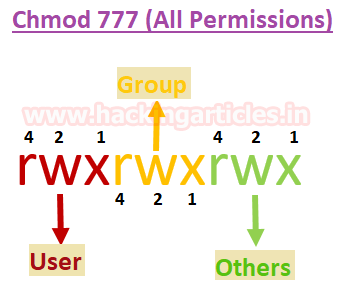
Linux Privilege Escalation Using Suid Binaries
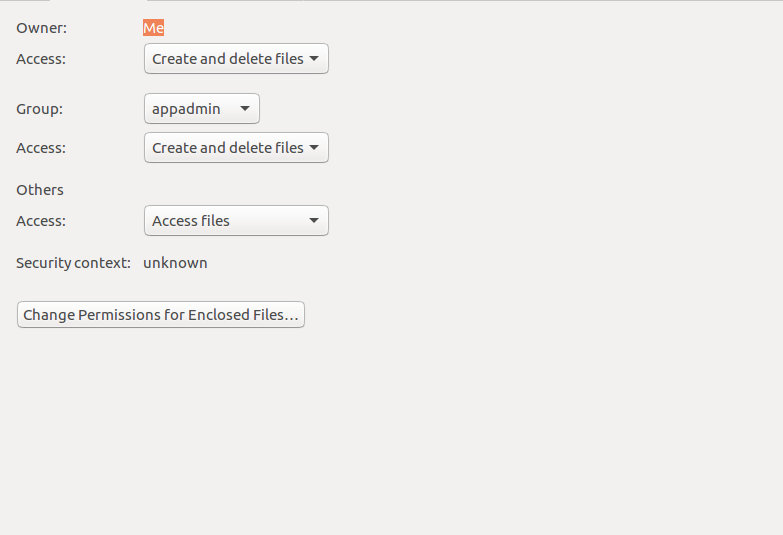
Chmod 777 What Does This Mean Learn Linux Permissions Easy Way

Give Write Access Chmod Unix

Chmod Why It Matters User Permissions In Os X Droppedframe Com

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Chmod Cheatsheet Linux

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

Linux Chmod Command Tutorial With Examples To Change Permission Of Files And Folders Poftut

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod
Chmod Command In Unix Unix File Permissions Chmod With Examples Chwn Command Chgrp Command Unmask
How To Deny File Permissions To Everyone Except Yourself In Linux Linuxhostsupport

Chmod Wiki Ask Ubuntu
Why Would Using Chmod 777 Recursively From The Root Cause A Linux Box To Not Boot I Could Understand This If I Were Limiting Permissions But Why Would Adding Permissions Cause This

Chmod Wikipedia

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

How Do Linux File Permissions Work

Give Write Access Chmod 644

Change File And Folder Permission On Ubuntu Chmod Chown Command In Linux Youtube

Permissions Why Use Chmod Instead Of Chmod U Rw Go R Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu

Chmod Ftp File Permissions Stadtaus Com

Linux Unix Permissions And Attributes Linuxsecrets
What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials
Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

User And Group Permissions With Chmod And Apache
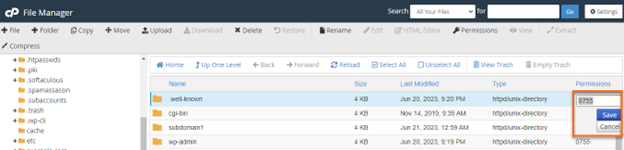
How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support
%20access%20permission%20%EC%98%88)%20chmod%20644%20test.jpg)
Permissions Why Use Chmod Instead Of Chmod U Rw Go R Unix Linux Stack Exchange
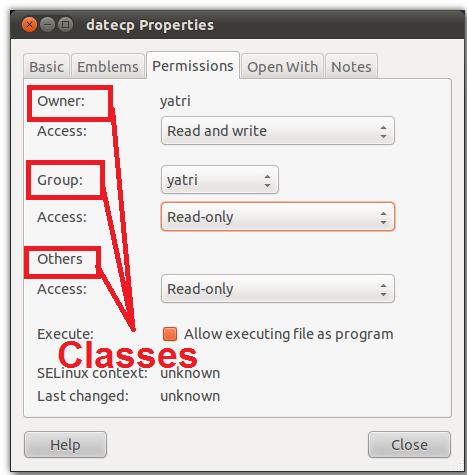
What Is Chmod 777

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode

Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech

Csc128 Permissions And Links Chmod And Ls

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux Basic Linux Permission Linux File Permission Wiz Maverick Benisnous

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions

Understanding File Permissions

Ownership And Permissions

Linux File Permissions Tutorial For Beginners

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Chmod Ftp File Permissions Stadtaus Com

Understanding Linux File Permissions With Chmod Umask Chown And Chgrp Liquidon Net

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
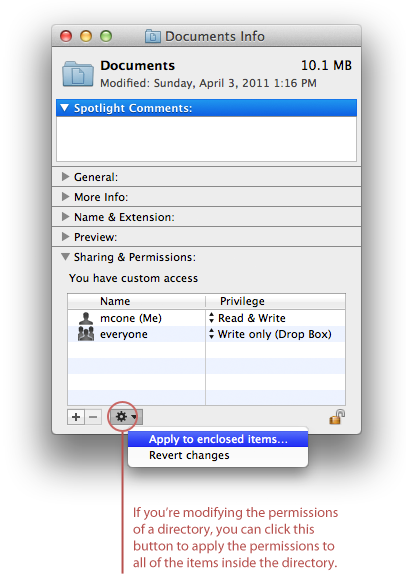
How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command Nixcraft

Solved Chmod Can Be Used To Change The Mode Of The File Chegg Com

How To Give Read Write Permissions To A Folder In Ubuntu Code Example

Changing File Permissions Wordpress Org
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example
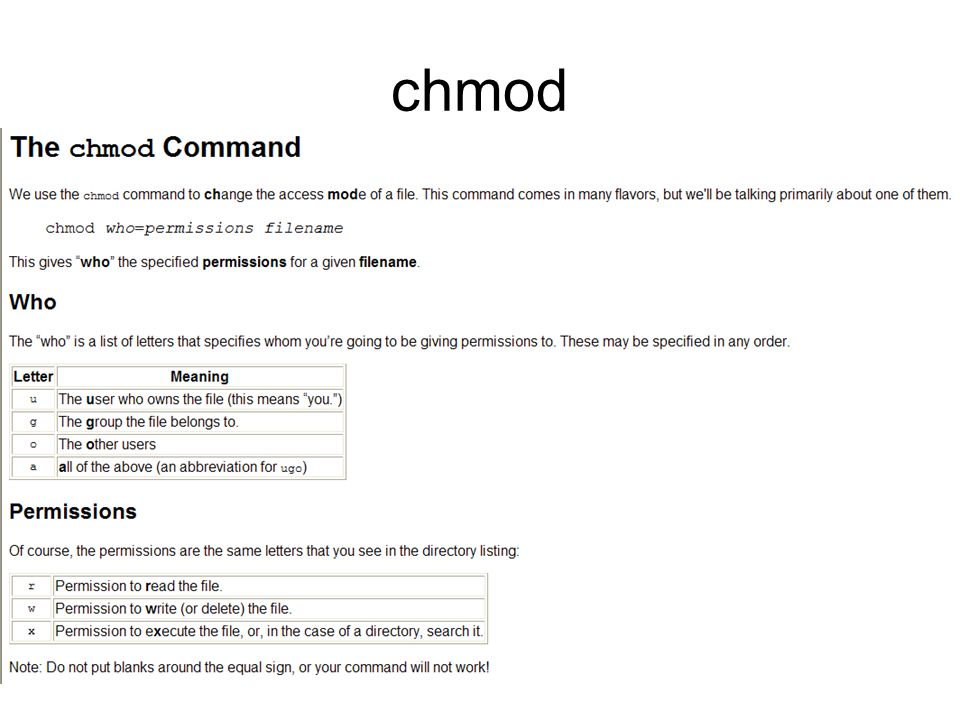
Chmod 0400 Means

Use Of Chmod Command In Linux Devopsdex

Understanding Basic File Permissions And Ownership In Linux The Geek Diary

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro

Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples

How To Modify The File S And Directories Permission In Linux Vasanth Blog

File Permissions Rhel 7 Tutorial

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux
Q Tbn 3aand9gcslbhvh5emm 4 Trrp3thfcmqosdrfzef Gvyldtqf1wtkgi37f Usqp Cau

Solved File Permissions In Linux Can Be Set Using A 3 Dig Chegg Com

Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Ppt Video Online Download

Changing File Permissions In Linux The Chmod Command By Saswat Subhajyoti Mallick Medium
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)
Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks
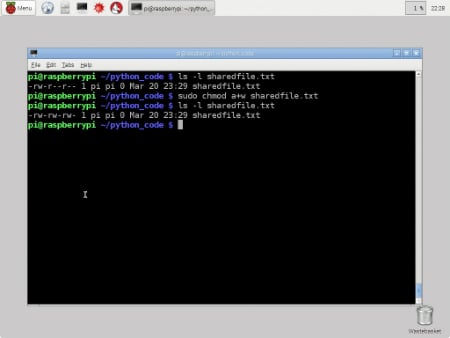
Working With File Permissions On Your Raspberry Pi Dummies

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Directory How Can I Change Permissions Of A Folder Including Its Enclosed Files And Subdirectories Ask Ubuntu
Linux Chmod Tips
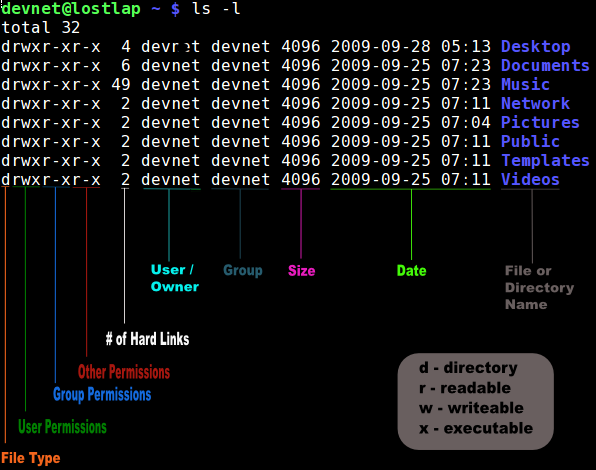
Chmod Archives Yet Another Linux Blog

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq2oq90gyu7qjtwwppsiodhgqotjbz3awrstnhczkm6hwgdiahx Usqp Cau
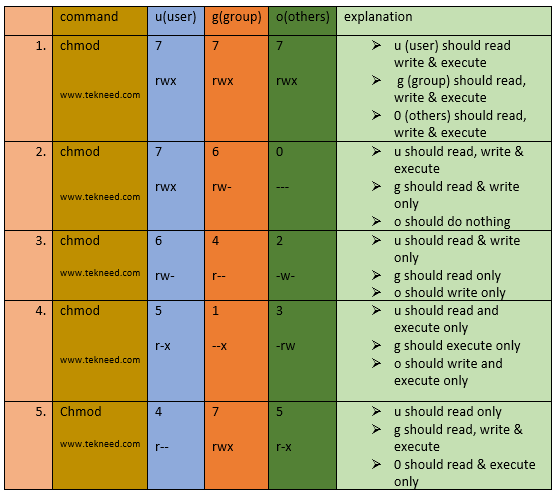
How To Set And Manage File Permission In Linux Part 1

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

How To Change Permissions And Owners Via Linux Command Line

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier



